
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Mechanic's automation tasks are written in Liquid, which is a template language used heavily in and around Shopify. This means that developers of all levels, with even a little Shopify development experience, can get started with Mechanic.
To find a developer for hire, you can contact Mechanic Partners directly at partners.mechanic.dev. This is a growing list of established developers, both independent and agency, who can help you with your implementation.
This is a super common path, and the Mechanic community is here to help. :)
If you already have a developer on your team, or have an existing connection to a developer, send them this article and see if they can help you!
Mechanic's task library is a compendium of e-commerce automation tasks and documentation, written by the Mechanic community and the Mechanic core team. Hosted on GitHub, everything is open-sourced under the highly permissive MIT license, making all library tasks appropriate for re-use and modification.
When building a new task, it's often easier to modify an existing task than to create a task from scratch. Searching GitHub is a good place to start, when looking for inspiration.
To browse the task library, visit tasks.mechanic.dev.
The Mechanic community can request new tasks – see Requesting.
The task library is open for contributions, by way of pull requests – see Contributing.
Mechanic was made for working together. Our Slack workspace is where hundreds of folx compare implementation notes, collaborate on projects, and talk about the evolution of Mechanic itself – and it's the best place to ask your questions. You are always invited. :)
These actions allow your Mechanic tasks to speak to other app and systems :) Use Mechanic to integrate your Shopify store with other apps like Airtable, Google, Slack, and more.
In Mechanic, an event represents anything that happens. This could be an order being paid, or a customer record being created, or a fulfillment being delivered.
An event always has a topic, and data (even if the data is null/nil). Event attributes may be referenced in Liquid using the Event object.
Events may trigger any number of tasks, resulting in any number of actions.
Events are fed into Mechanic by the responsible party – for events that are about things in Shopify, for example, the events come to Mechanic from Shopify itself.
I'm glad you're here. :) –Isaac
Mechanic is a Shopify development and automation platform.
for an off-the-shelf solution
for a task that fits you perfectly
if you need something else
Important Notice
Shopify is deprecating the Shopify Admin REST API which the Mechanic REST objects depend on. The first round of deprecations involve the product and variant endpoints. Read about the deprecation and .
Use the going forward. The and objects will cease to work on on Feb 1, 2025 due to the changes being made by Shopify. Shopify will phase out the REST API completely over time, you can read more about this .
In specific cases, events may be triggered by activity associated with an earlier event. In these scenarios, we describe the subsequent event as a child event, and the preceding event as a parent event.
The generates a new child event, when performed
A subscription to the topic generates new child events as actions are performed
Tasks responding to child events may reference to the parent's event using {{ event.parent }}
Mechanic tasks may be imported and exported as JSON, using the "Import" or "Export" button below the task editor. The JSON schema used for representing tasks is identical to that used by the task library, making it suitable for .
Mechanic has the ability to import tasks from JSON individually and in bulk, from the "Import tasks" screen.
Each task loaded via this route may be saved as a new task, or – if the task name exactly matches the name of a task already in the Mechanic account – it may be saved over the existing task. This latter path provides a way for batches of updated tasks to be loaded into a Mechanic account all together, preserving the version history for each task.
A task's code is a template. In the same way that a Shopify storefront might use a Liquid template to receive requests and render HTML, a task uses its Liquid code to receive events, and render a series of JSON objects. These JSON objects define , , and .
For every Shopify resource object that supports metafields, Mechanic has traditionally provided a way to directly access those metafields from the resource using . This shortcut will no longer be accessible for product and variant REST resources once they are fully deprecated.
While metafields can be queried directly using their ID, this attribute is not present in the product webhook data. The standard approach in GraphQL is to query the product resource for the metafield(s) and value(s), passing the namespace and key as the "key" value, in the same manner as the REST dot notation lookup.
Mechanic's works asynchronously, performing as much work as possible, as quickly as possible. However, there are cases where it's important that actions run in a sequence – one after the other.
We support this with an advanced task setting called "Perform action runs in sequence", configured in two parts:
Perform action runs in sequence – When enabled, Mechanic will only run one of the task's resulting actions at a time, performing them in the order in which they were generated.
Halt the sequence when one fails – When this option is also enabled, Mechanic will only run the next action if the current action was performed successfully. If the action fails, all following actions will be marked as failed as well, with error messages explaining the situation.
Each task is configured with a specific , defaulting to the latest version at the time of the task's creation.
This version is used in all activity related to the current task, including:
REST API calls performed to support Liquid lookups
GraphQL calls performed by
Shopify uses webhooks to notify apps like Mechanic about new activity. Mechanic supports every type of Shopify webhook in its set of . By setting up to these topics, a task may respond to any supported type of Shopify activity.
Note that Shopify does not strictly guarantee webhook delivery. See for more on this subject.
A task may enforce custom validation for options by including validation logic in its code, inspecting the current value of an option and rendering an if the option does not meet its criteria.
A modification to a task option will always result in a new being rendered. In this way, a task developer may provide the user with immediate feedback on their task configuration.
In this example, a task begins by validating an option called "A positive number". The only flags on this option are "required" and "number", meaning that Mechanic's involvement is limited to making sure the user fills in this task option with a number.
The plaintext file generator is used implicitly, when a JSON string is given in place of a standard file generator JSON object. The resulting file will contain the content of the string, with no further processing. This makes the plaintext generator suitable for text files, CSV files, TSV files, and any other file format that can be expressed using plain text.
The plaintext generator cannot be invoked explicitly; "plaintext" cannot be used as a named generator type.
Because this file generator is used implicitly, when a string is given instead of a file generator object, this file generator does not use options.
When a task renders an error object, the task run will be marked as failed, and no rendered action runs will be performed. This is a good way to communicate an intentional failure to the user, when your Liquid code detects a certain condition.
A task that renders an error object will interrupt the preview, and visibly communicate the error to the user. This makes error objects a useful way to validate .
Unlike a "raised" exception in other programming languages, a rendered error object is simply added to the list of the task run's JSON objects. At the completion of task code rendering, all objects are evaluated; at that point, if an error object is among them, the error is then raised and shown to the user.
Log objects are useful for recording information for later reference. They have no side-effects. Carefully chosen log objects can massively simplify post-hoc debugging, especially (as we've found) when investigating merchant bug reports.
A log object is a plain JSON object, having the following structure:
The log details can be any JSON value.
Log objects are most easily generated using the .
Log objects appear wherever task run results are visible, including the task preview and when viewing an event.
Mechanic supports several methods of reading data. The following articles discuss usage, and when each technique might (or might not) be appropriate:
The allows developers to submit any request to the Shopify Admin API. By , the data returned by Shopify can be retrieved, and re-used by the calling task.
This approach should (probably) only be used as a last resort, when Mechanic's other methods of do not cover the scenario.
Use the to read data. Use the to write or update data.
{% action "files" %}
{
"plain.txt": "This\nis\na\nmulti-line\nplaintext\nfile."
}
{% endaction %}Task code always has access to a set of environment variables, which can be used to make decisions about what JSON objects to render.
A task must purposefully consider its preview, so as to accurately communicate its intent to users and to the Mechanic platform.
Community Support: We encourage you to join our Slack community, where you can seek advice and share experiences with other Mechanic developers. Often, community members can offer insights or solutions based on their experiences.
Joining the Community: You can join our Slack community through the following link: Mechanic Slack Community.
Partner Directory: We recommend hiring a developer if the issue requires more in-depth technical expertise. Our partner directory lists qualified developers familiar with Mechanic task development.
Finding a Developer: Visit our partner directory at partners.mechanic.dev to find a developer who can customize or optimize your task. If you want to be matched with a suitable developer, use our matchmaking service.
Shopify's "update" webhooks do not contain information about what piece of data has changed. (For example, a product update webhook does not specify what attribute of the product has changed.) For this reason, it's not possible to subscribe to changes in specific resource attributes (like product SKUs, or order tags).
If a task needs to react to a specific attribute change, the task must scan for and "remember" the original value of that attribute, so as to compare incoming updates with that remembered value. A task could use the Cache action to store these values in the Mechanic cache, or it could use the Shopify action to save the remembered value in a metafield.
For an example implementation, see the Auto-tag products when their variants change task.
There is a single correct answer for writing data to Shopify: the Shopify action. :)
{% assign metafield = product.metafields.custom.my_field %}
{% if metafield.value == "Alpha" %}
{% log "metafield value matched" %}
{% endif %}{% capture query %}
query {
product(id: {{ product.admin_graphql_api_id | json }}) {
metafield(key: "custom.my_field") {
value
}
}
}
{% endcapture %}
{% assign result = query | shopify %}
{% assign metafield = result.data.product.metafield %}
{% if metafield.value == "Alpha" %}
{% log "metafield value matched" %}
{% endif %}{
"log": LOG_DETAILS
}

{% if options.a_positive_number__required_number <= 0 %}
{% error "The option 'A positive number' must be greater than zero." %}
{% endif %}
{% action "cache", "set", "a_positive_number_to_remember", options.a_positive_number__required_number %}This also means that rendering an error object will not prevent the task from reaching any syntax errors (or other problematic code) later on in the task's Liquid code.
An error object is a plain JSON object, having the following structure:
The error details can be any JSON value. This value will be represented to the user as the reason for the task failing.
Error objects are most easily generated using the error tag.
{
"error": ERROR_DETAILS
}Find Mechanic on the Shopify App Store: apps.shopify.com/mechanic
Mechanic is a Shopify development and automation platform, which comes with a rich library of pre-written automation tasks – and our users write their own custom tasks every day. Let's find out if Mechanic might work for you.
Are you working on something Shopify-related?
Mechanic is only available for Shopify.
Is what you're looking for already available from Mechanic's task library?
We have hundreds of common scenarios already handled with pre-written, open-source, modifiable, off-the-shelf tasks.
As far as your problem concerns Shopify data, is what you want to do supported by the ?
Mechanic's toolkit goes beyond Shopify's APIs, but a Mechanic task can only interact with Shopify data in ways that Shopify supports.
Are you open to ?
Whether you need a developer or already have that covered, the path to creating a custom Mechanic task is well-established.
That list wasn't exactly a formal flowchart, but we hope it's helpful as you're evaluating Mechanic for your purposes. At its best, Mechanic is a platform and toolkit that you go to, and return to, when you hit the limits of the Shopify admin. And it's a community that collectively has learned how to solve many, many kinds of problems. (Join our community Slack workspace!)
A developer writes tasks – Mechanic's term for a piece of automation. These tasks can respond to many different events, like a Shopify webhook, a manual trigger, a regular interval (e.g. hourly, daily), or an incoming email. Tasks use subscriptions to signal their interest in specific event types.
When a task receives an incoming event, it can choose to generate an action – an operation that has an effect.
The Shopify action makes changes to a Shopify store, like tagging, publishing, creating or deleting resources. It provides direct and complete access to Shopify's admin API, with support for both REST and GraphQL.
The Email action is for sending email. It supports custom templates, and attachments.
The FTP action is for uploading files to an FTP or SFTP server. These files may be generated by the task, or can be fetched from external locations.
The action performs any request, to any HTTP endpoint. This facilitates integration with third-party APIs.
The action generates a variety of file formats, including PDF, CSV, ZIP, and anything retrieved from a public URL. Files generated this way receive a temporary URL of their own, and can be fed into other tasks for further processing.
For a complete list of supported actions, see Actions.
Mechanic makes heavy use of Liquid – a template language created by Shopify. Its primary use is in task code. In the same way that a Liquid theme receives browser requests and renders HTML, a Mechanic task receives events, and renders actions (by defining them with JSON).
In Mechanic, our Liquid implementation includes additional support for constructing arrays and hashes, and includes many useful filters, making data processing more efficient.
Mechanic performs work using queues of runs, with no limit on how large each queue can become. If there is a sudden surge of incoming events for a Shopify store, the store's dedicated Mechanic queue could become delayed. This is an important difference between Mechanic and many other systems: in a high-traffic period, Mechanic will never refuse incoming events for a store; instead, it will process each one as soon as possible, by putting them into a run queue. The rate at which Mechanic processes work varies, depending on concurrency and the Shopify API rate limit.
Tasks that are useful foundations for developers, for further modification or inspiration
The Mechanic staff commission these from developers in the Mechanic community. If you're a developer interested in receiving this kind of work, get in touch at [email protected].
Head to https://mechanic.canny.io/task-requests. :)
Understanding the Shopify GraphQL schema Familiarize yourself with the Shopify GraphQL Admin API objects, queries, and mutations.
Review how to use GraphQL in Mechanic Start here and peruse the task library to see examples of GraphQL usage in tasks.
Identify REST usage within a task
Broadly, any usage where one Liquid REST object is used to reference another Liquid REST object with dot notation. This does not include fields on the original REST-like webhook resource (e.g. product.title).
For the product and variant resource deprecations specifically, this includes:
shop.products
shop.variants
collection.products
inventory_item.variant
Field mapping: Identify the objects, fields, and nested structures needed in GraphQL based on the existing REST usage within a task. Build and validate queries using .
Update Mechanic task code : Replace the relevant REST calls with Mechanic-flavored Liquid GraphQL query and result objects (see the tutorials following this page for examples).
Testing: Trigger the updated task to make sure it returns the expected results and/or takes the expected actions.
The product webhook does include an array of images and variants in the product JSON which will still be accessible via dot notation. Note that these are not the same as the previously available Mechanic REST lookups for those resources.
The images and variants data arrays should be used with caution once Shopify releases support for 2 thousand variants per product, in conjunction with the product and variant REST endpoint deprecations. The product webhook will only include full detail for the first 100 variants. It is not yet clear what Shopify will do with images in the product webhook.
{{ event.parent.parent.parent }}When viewing any given event in Mechanic, look in the event details to find any parent or child relationships that apply. Click through to any displayed parent or child event to view that event's details.
Subscriptions
Code
As written, this task will "fan out": it will generate 1 child event, which will then generate 2 child events, each of which will then generate 3 child events, and each of those will then generate 4 child events, and finally, each of those events will generate 5 child events of their own. The result: 154 events, created with a single click. 💪
Importantly, note the "task_id" option, applied to the Event action. This option ensures that only this task, and no other, will respond to the new event. While it's unlikely that any other task will subscribe to "user/fan/out" events, this option is important for ensuring expected behavior.
mechanic/user/trigger
user/fan/outOn the next screen, follow the prompts to load your JSON task exports into Mechanic.
When working in the task editor for a specific task, use the "Import" button to load in task JSON and have it applied to the current task.
When viewing the task list on the Mechanic home screen, use the "Export" button after selecting one or more tasks to copy a JSON export of all tasks to the clipboard. This export can be used with Mechanic's task import area, described above.
When working in the task editor for a specific task, use the "Export" button to copy a JSON representation of the current task to the clipboard.
Action run sequences are enforced within each task run. This means that a task could see more than one of its actions performed at the same time, if the task itself were to run multiple times, simultaneously.
To explain by example: a task that responds to mechanic/scheduler/10min, generating a sequence of 5 actions that each take 1 minute to run, will never see those actions overlap. However, if the task generated 15 actions instead, the actions would begin to overlap, as the task generates 15-minute action sequences every 10 minutes.
All Shopify API versions are named with a specific date (i.e. "2021-07"), except for "unstable". This version receives regular updates from Shopify, and its features may change without notice.
Most tasks should use a dated version, to maximize the amount of time a task can rely on a specific set of Shopify API features.
Shopify supports each version for 12 months (except for "unstable", which is always available). 30 days before a task's version becomes unsupported, Mechanic will automatically begin calling the closest supported version instead.
Shopify may, at times, mark certain API features as deprecated. If a Mechanic account calls a deprecated API, Mechanic will display the deprecation notice in the app. Learn more about Shopify API deprecations.
The selector for a task's Shopify API version is available in Advanced mode, below the task code area.
Until further notice, Shopify will continue to send product webhook data in a REST-like format. Tasks that only use the fields available in the webhook (e.g. product.title) may not need to be converted by the deprecation notice date. However, if connections to other resources are made from that product (e.g. product.collections), then that will require conversion.
This is a simple task to loop through a product's collections, check if the collection contains a certain tag, then log out the collection title.
{% for collection in product.collections %}
{% assign collection_tags = collection.tags | split: ", " %}
{% if collection_tags contains "my-tag" %}
{% log collection_with_my_tag: collection.title %}
{% endif %}
{% endfor %}The GraphQL version of the the task above use a paginated query to get all of the collections a product is a member of. The outer loop upper range (e.g. the 10 in {% for n in (1..10) %}
) is arbitrary, and you may adjust it to the approximate maximum number of collections any given product might have.
The event preview block in this task sample makes this code appear to be overly verbose, however the preview block is often an important step to ensure that Mechanic prompts for the correct scopes for reading and writing Shopify API data.
Great! Mechanic is made for this. Here's where to start. :)
Mechanic is a development platform – in the hands of a developer, it can be used to accomplish almost anything in Shopify. While our task library covers many use cases, Mechanic's true strength is in letting developers solve merchant problems quickly, giving merchants easy configuration forms for managing the resulting tasks.
Tread lightly! We've got notes on this here: .
Mechanic's automation tasks are written in Liquid, which is a template language used heavily in and around Shopify. This means that developers of all levels, with even a little Shopify development experience, can get started with Mechanic.
To find a developer for hire, you can contact Mechanic Partners directly at . This is a growing list of established developers, both independent and agency, who can help you with your implementation.
Lastly: if you already have a developer on your team, or have an existing connection to a developer, send them this article and see if they can help you!
If you're familiar with Liquid, and Shopify's Admin APIs, start by picking something from our that's close to what you're looking for, then modify it as needed.
Make sure to take advantage of the documentation found here, beginning with the section. Mechanic is a powerful system, and grounding yourself in the fundamentals is a good way to begin.
Finally, join Mechanic's to exchange support with the community. The #general channel is a great place to start, and it's filled with people who are using Mechanic to solve problems every day. :)
Shopify does not offer a strict guarantee on webhook delivery. In rare cases (and usually in high-volume situations), we've observed Shopify fail to send a webhook.
Quoting from Shopify's recommendation for this scenario:
Your app shouldn't rely solely on receiving data from Shopify webhooks. Because webhook delivery isn't always guaranteed, you should implement reconciliation jobs to periodically fetch data from Shopify.
This applies to Mechanic tasks as well (which are, essentially, tiny apps).
For tasks that respond to events on Shopify resources, we recommend the following, using shopify/orders/create as an example:
Update the task code to mark orders as having been processed. This could take the form of an order tag (e.g. "processed-by-task-xyz"), or a metafield. Additionally, ensure that this code skips orders that are already marked as processed.
Add a , like mechanic/scheduler/15min. Then, update the task code so that these scheduled runs are used to scan for and process new orders in the last 15 minutes that have not yet been processed. This is the reconciliation step, ensuring that all new orders are ultimately processed, one way or another.
Hey there! :) I'm Isaac, the creator of Mechanic. Those two lines above are the most important things to know. Keep reading if you're curious.
AI makes it super easy to create code. This is awesome. I'm so, so excited about this. The more the merrier.
This means Mechanic needs to learn something too: how to work with AI coders that can easily produce well-formed code but might not understand the patterns that Mechanic itself strictly abides by.
An AI can rapidly produce code, and it'll be good-looking code, but if the AI doesn't understand Mechanic the code might not work at all. In a very real way, it becomes a case of Mechanic not understanding the AI.
This is an interesting bind: because AI changes faster than Mechanic, it becomes a question of how best to guide the AI. For folks who understand code less than the AI, this puts everyone in a rough position: the AI is doing its best but can't tell when it doesn't understand, and the human is doing their best but can't tell when the AI doesn't understand, and all Mechanic knows is that it's being given something it doesn't understand.
As of this writing (currently June 12, 2025), AI is getting better at Mechanic. It's definitely getting better. But, still:
AI code often "invents" Mechanic features that do not exist (like writing task code in YAML, or compiling action objects into a JSON array)
AI code often fails to invoke necessary Mechanic features (like !).
Intelligence is a game of guessing intelligently: AI often sort of just guesses at what task code is supposed to generate.
Mechanic, as a platform, is a place for solving things together. "Together" works best when everyone's honest about where they're at. Mechanic's a good place for that. :)
The AI path with Mechanic is getting better, but it's not smooth yet. If you're having trouble with this, head to — that page has an overview of the smooth paths that do exist.
To learn about how we at Lightward Inc roll with AI, please visit , and say hello. :)
No matter what: thank you for being here. ❤️
=Isaac
In some cases, a run that has already been performed may be performed again, using a retry.
When a run is retried, its previous result is permanently discarded. Because of this, runs that already have a meaningful result (i.e. an event run that gave rise to task runs, or a task run that generated actions, or an action run that succeeded) cannot be retried.
Runs are given automatic retries when a non-permanent error is encountered. In some cases, Mechanic permits manual retries for runs, allowing users to reset a run's result and perform the run again.
Retried event runs will always reflect Mechanic's current configuration, including any .
Retried task runs will always use a task's latest configuration, including the task's , , and .
Retried action runs will always use their original action options, as dictated by the task run that generated them. Action runs are entirely unaffected by updates to their task.
When non-permanent errors are encountered, Mechanic will automatically retry a run. For , this might be a connection error. For , this might be a temporary outage with our email provider.
Mechanic will automatically retry these runs up to 4 times, for a total of 5 attempts. Retries are subject to a variable backoff delay, of approximately 0:30, 1:16, 2:32, and 5:08 respectively, for each of the 4 retries.
Some task runs may be manually retried, via the Mechanic user interface.
Task runs may be retried...
... if the task run itself failed (due to a Liquid error, an API error while reading data, or something else)
... or, if the task run did not generate any actions
During task development, it can be useful to set up a task to only render . A task run which only rendered log objects can be retried, and this ability to retry can be convenient when rapidly iterating on task code.
Only failed action runs may be retried.
The URL file generator accepts a string as its options, containing a valid URL. This generator downloads the file at that URL, returning the results.
Downloaded files may be a maximum of 20 megabytes, even when used within other file generators (like ZIP).
This file generator accepts a string containing a valid HTTP or HTTPS URL. It does not support any other options.
{
"url": URL
}In general, Mechanic's run system does not guarantee the execution order for runs that have been created at the same time (see Concurrency). This applies to all kinds of runs: events, tasks, and actions.
For tasks, the simplest way to manage this is by using subscription delays, offsetting the time at which each task is run. For example, if you have two tasks that subscribe to shopify/customers/create, you might adjust one so that it it subscribes to shopify/customers/create+10.minutes instead. This way, your first task has a chance to execute and run before the other.
This is not a perfect solution: naturally, if the first task takes more than 10 minutes to run, there will still be overlap. So, Mechanic makes
Each task has an advanced option called "". When this is enabled, all generated actions for a given task run will be executed precisely in order.
The best tool to leverage here is the , coupled with action sequences (see above).
Begin by making a list of the tasks for which you need to guarantee run order, sorted by the desired run order. For these purposes, all of these tasks should subscribe to the same event topic.
Beginning with the task that should run first, (a) enable "Perform action runs in sequence", and (b) add an "event" action at the very end of your task script. The intent here is for this action to kick off a unique event topic that the second task should the subscribe to.
Having added that "event" action, update the second task so that it subscribes to your new event topic, instead of the original event topic. If there is a third task that should follow this one, repeat step 2 for this task as well, in preparation for kicking off the third task.
One more tool is worth mentioning: tasks may subscribe to mechanic/actions/perform to be re-triggered when each of their own actions are performed. For more on this strategy, see .
The Echo action has no effects: it returns the options that are given. This action can be useful for testing or debugging, by temporarily replacing some other action with an Echo action having the same options. In this way, a developer can safely get feedback on what data is in play, without side effects.
This action accepts any and all options, restricted only in that they must be valid JSON values (as with all results of task code).
If the Echo action is given a "__error" option, it will raise that error when the action run is performed. Use this feature when it's useful to indicate an issue with a task run, without marking the entire task run as a failure (as would be the case when using an ).
When a task subscribes to the mechanic/user/form event topic a "Run task" button is added to the task.
When the Run Task button is clicked the user is presented with a form that contains any task options that have the _userform flag.
When submitted, an event is generated, to which only this task will respond. The event contains the user's input in its data, making user's input available in event.data.
During a mechanic/user/form event, the ad-hoc values arrive under event.data.
A task's Liquid code always has access to a set of environment variables, defined by Mechanic.
An oft utilized feature of Mechanic is the ability to add Liquid tags into task options fields, such as a configurable email body. Additionally, these Liquid tags (currently) support inline resource lookups for data not available in the event webhook. However, for products and variants this will no longer work as of the .
The code above could be utilized directly in a . and it would output a string of text (e.g. "Special product notice for Widget - Red...") into the assigned option field variable.
One method of conversion for lookup fields is to utilize a GraphQL query directly in the option field, which naturally has some caveats.
Event preview blocks are not evaluated in task option fields. Instead, default values should be assigned to any webhook fields utilized by the query (e.g. product.admin_graphql_api_id). This will keep the task parser happy and allow you to save the task. Be careful though to not assign a default value to a webhook field that can have a null or blank string as a valid value.
A task subscription is the expression of a task's intent to receive certain , filtering by . A subscription consists of an event topic, optionally combined with a time offset, which creates a delay.
A task may have any number of subscriptions.
... are accomplished using subscription offsets, as described below. This heading is here for folks searching for a way to delay their tasks. ;)
In this tutorial, you'll learn how to create a feed of your shop's data, and make it available on your online store, at a URL like https://example.com/pages/feed
Tip: The data you generate can be imported directly into Google Sheets. Learn more:
This technique has several limitations:
In Mechanic, a task is a bundle of logic and configuration, that responds to and interprets . The result of a task can define , which are the task's opportunities to have an effect on the world.
A task responds to events based on its . When an event is received that matches a subscription, the task processes the event using its . The code has access to the event data; it also has access to the user's task configuration, through . Task code is written in Liquid, and is responsible for rendering a series of JSON objects (including , , and objects), defining work to be performed once task rendering is complete.
A task uses its to communicate ahead of time the work it intends to do. Previews are important for users, and are also important for Mechanic itself – Mechanic looks to the task preview to understand what permissions a task requires.
Tasks may be written from scratch, or installed from the Mechanic library (available in-app and ). Once installed, a task's code may be modified at any time.
To make events easy to identify, each event has a topic. Tasks signal their interest in specific event topics using .
A topic looks like "shopify/customers/create", and it has three parts:
The domain describes the source of the event. Shopify events have "shopify" as their domain, and events generated by Mechanic itself use "mechanic".
The subject describes the type of resource the event describes. Events that are about customers have "customers" as their subject, and events that are about orders have "orders".
In general, Mechanic will process as many simultaneously as possible. This means that multiple tasks subscribing to the same event topic are very likely to execute simultaneously, when such an event occurs.
To protect the health of the system and to ensure performance for every store on the platform, Mechanic have several concurrency limits, defining the conditions in which Mechanic will perform runs simultaneously.
{% assign n = event.data | default: 0 | times: 1 %}
{% if n < 5 %}
{% for m in (0..n) %}
{% action "event" %}
{
"topic": "user/fan/out",
"data": {{ n | plus: 1 | json }},
"task_id": {{ task.id | json }}
}
{% endaction %}
{% endfor %}
{% else %}
{% action "echo", event_data: event.data, parent_event_data: event.parent.data %}
{% endif %}Make sure that any existing tags on the customer's account are kept, not lost
Use the REST API for this operation
Use a static preview action, to show the merchant a preview of what the task will do
inventory_level.variant
line_item.product
line_item.variant
product.collections
product.images *️
product.metafields
product.variants *️
variant.inventory_item
variant.inventory_levels
variant.metafields
variant.product
Repeat until you reach the final task in your list. This task does not need an "event" action at its conclusion; it only needs to have its subscription updated to listen for the penultimate task's generated event.
Event runs may be scheduled using the Event action, using its run_at option to define the time at which the run should be performed.
The task runs that arise from a scheduled event run will not be established until the event run is performed. (This does not apply if the task_ids option is used, which determines ahead of time which tasks may be run in response to the new event.) This means that changes to the set of enabled tasks can have an impact on what tasks are actually run, in response to a scheduled event run.
Mechanic supports several scheduler topics (such as mechanic/scheduler/hourly), allowing tasks to be automatically invoked by the platform on a regular repeating interval.
Event runs generated in response to scheduler events are always adjusted for the store's local time.
Task runs may be scheduled using subscription offsets, in which a task states that it wishes to run later (by some amount of time) than the event that triggers it.
Subscription offsets are a property of the task, and are applied by the task run – not the event run. This means that the subscribed-to event must be created and run before the subscription offset is calculated and applied.
To achieve precise scheduling (e.g. "run on December 16th at 2:30pm"), or to accomplish scheduling for an interval not supported by Mechanic's scheduler topics, use the Event action to schedule an event run at any chosen time, with a custom event topic. Make sure that the desired task is subscribed to the same custom topic, and consider using the Event action's task_id option to specify that only the desired task is allowed to respond to the new event.
Task runs that are scheduled for the future will always use a task's latest configuration, including the task's options, code, and Shopify API version.
If a task is disabled or deleted at the time a task run comes due, the task run will still perform at the scheduled time, but will fail instantly.
The verb describes what has just occurred. Events that are about creating resources generally have "create" as their verb, and events that are about deleting resources generally have "delete".
The User event domain is for custom, user-generated events, having any subject and verb (e.g. "user/foo/bar"). As with all events, a User event topic must use the standard three-part topic form, but only the "user/" prefix is mandatory.
Mechanic allows developers several ways to generate custom User events:
The Event action can be used with any User event topic
Webhooks may be configured to generate events using any User event topic
Each store's Mechanic account has a fixed run queue size. This limit controls how many runs Mechanic will perform simultaneously for your store. With a limit of 2, this could mean 2 events, or 2 tasks, or 1 event and 1 tasks and 0 actions, or any other combination of runs. Additional runs will be performed as the preceding runs complete.
Use GraphQL to query Shopify, to keep your data usage efficient. (To learn more, see Interacting with Shopify.)
For options for ordering execution of runs, see Ordering.









{% action "files" %}
{
"image_from_url.png": {
"url": "https://www.google.com/images/branding/googlelogo/2x/googlelogo_color_272x92dp.png"
}
}
{% endaction %}A subscription offset (sometimes called a delay) defines the amount of time a task should wait or delay (!!) before responding to the incoming event. It's the easiest way to add a delay to a task's subscription to a specific topic. (For finer control over event timing, try using the run_at option of the Event action.)
Subscription offsets are appended to the subscription topic, and are of the form "+1.hour". Offsets may be given using seconds, minutes, hours, days, weeks, months, or years. There is no limit to how large the subscription offset may be.
A subscription with an offset looks like shopify/customers/create+1.hour.
To learn more about scheduling work with Mechanic, see Scheduling.
In practice, large offsets can make debugging difficult! If you're thinking about work to be done weeks or months or years from now, consider running an hourly or daily task that scans for work that's due to be done, instead of scheduling tasks for the distant future.
The \[Shopify variables]\(code/environment-variables.md#shopify-variables) available to tasks always contain data drawn from the event itself. If a task has a offset event subscription, this data may be outdated by the time the task runs.
To reload the data in a Shopify variable, use something like this:
Remember, Mechanic does not permit access to the Shopify API during event preview. Using this unless statement ensures that reloading only happens during a live event.
A task's subscriptions are parsed for Liquid, at the time the task is saved. Combined with task options, this is an opportunity to generate subscriptions based on user configuration, adding or removing subscriptions based on the user's choice, or adjusting subscription offset based on a user-entered value.
One subscription is permitted per line. Blank lines and leading/trailing whitespace are permitted.


{% action "echo", __error: "Forcing an error!" %}
{% unless event.preview %}
{% assign customer = customer.reload %}
{% endunless %}shopify/orders/create
{% if options.send_email_when_order_cancelled__boolean %}
shopify/orders/cancelled
{% endif %}shopify/orders/paid+{{ options.days_to_wait_before_followup__number_required }}.daysshopify/customers/create{% if options.wait_one_hour__boolean %}+1.hour{% endif %}{% assign cursor = nil %}
{% for n in (1..10) %}
{% capture query %}
query {
product(id: {{ product.admin_graphql_api_id | json }}) {
collections(
first: 250
after: {{ cursor | json }}
) {
pageInfo {
hasNextPage
endCursor
}
nodes {
id
title
tags
}
}
}
}
{% endcapture %}
{% assign result = query | shopify %}
{% if event.preview %}
{% capture result_json %}
{
"data": {
"products": {
"nodes": [
{
"collections": {
"nodes": [
{
"id": "gid://shopify/Collection/1234567890",
"title": "Widget collection",
"tags": ["my-tag"]
}
]
}
}
]
}
}
}
{% endcapture %}
{% assign result = result_json | parse_json %}
{% endif %}
{% for collection in result.data.product.collections.nodes %}
{% if collection.tags contains "my-tag" %}
{% log collection_with_my_tag: collection.title %}
{% endif %}
{% endfor %}
{% if result.data.products.pageInfo.hasNextPage %}
{% assign cursor = result.data.products.pageInfo.endCursor %}
{% else %}
{% break %}
{% endif %}
{% endfor %}{% action "echo", foo: "bar", baz: "qux" %}{% action "echo", "foo", "bar", "baz" %}{% action "echo", "foo" %}{% action "echo" %}
{
"foo": "bar",
"baz": "qux"
}
{% endaction %}{% # These will appear on the run task user form %}
{% assign big_event = options.the_big_event__date_userform %}
{% assign color_for_big_event = options.color_for_big_event__color_required_userform %}
{% # This will NOT appear on the run task user form %}
{% assign level = options.level__select_o1_low_o2_high %}
{% if event.topic == "mechanic/user/form" %}
{% # we need to get the value from event data, we don't want the value from the task option %}
{% assign big_event = event.data.the_big_event__date_userform %}
{% assign color_for_big_event = event.data.color_for_big_event__color_required_userform %}
{% endif %}
{% action "echo" big_event, level, color_for_big_event %}event
An object containing information about the current event
cache
The current store's object, supporting lookups for cached values
task
An object containing information about the current task
options
An object containing task , configured by the user
When a task is actually invoked for an event, it may have access to an additional variable, determined by the specific event it is responding to. When this is the case, the additional variable will be named after the event subject, and its contents will be established by the event's data. The name of this variable is communicated by the Mechanic task editor, based on the task's current subscriptions.
For example, a subscription to shopify/customers/create will make available a variable called customer. A subscription to shopify/products/update will expose a variable called product, etc.
All Shopify events support an additional variable named after the event topic. For example, when a task responds to a shopify/customers/create event, it will have access to an additional variable named customer, containing the customer data contained in the event.
Shopify events always contain data from Shopify's REST representation of each resource; therefore, automatic Shopify variables always contain data from the REST representation as well. The best resource for the data available for each variable type is Shopify's REST Admin API reference.
Shopify variables in Mechanic do not necessarily contain the same attributes as Liquid variables used in Shopify (in places like themes or email templates) – even if they share the same name.
In Mechanic, Shopify variables always contain data from Shopify events, which are delivered to Mechanic via webhook. This means that Shopify variables always have the same data structure as Shopify webhooks, corresponding to Shopify's REST representation for this data.
For example, while Shopify themes support customer.name, Mechanic does not (because Shopify's REST representation of the customer resource does not contain a "name" property). On the other hand, Mechanic supports customer.created_at, while Shopify themes do not.
shop
An object containing
It can be helpful when using a GraphQL query in a task option field to add the code flag to the option field, which will add line numbers and give access to Mechanic code snippets.
{%- assign qualifying_product = nil -%}
{%- for line_item in order.line_items -%}
{%- if line_item.product.product_type == "Special" -%}
{% assign qualifying_product = line_item.product -%}
{%- break -%}
{%- endif -%}
{%- endfor -%}
{%- if qualifying_product != blank -%}
Special product notice for {{ qualifying_product.title }}...
{%- endif -%}{% assign email_body = options.email_body__multiline_code_required | strip | newline_to_br %}Shopify doesn't support delivering the feed contents as plaintext. To get technical, this means that the feed will always be delivered with a content type of text/html.
Because this task stores feed values as a shop metafield, feeds created with this technique may only contain and display up to 65,535 characters.
To move beyond these, consider using the FTP action to upload your feed to your own server.
Start with our example task, using the "Try this task" button to add it to your account:
Immediately after adding the task, run it by clicking the "Run task" button. This will populate your shop's records with the initial value of the feed.
This task replicates Shopify's own product inventory CSV export. Feel free to make changes to the script, and don't hesitate to get in touch if you have questions. :)
This is the template that will be responsible for displaying your feed contents, without the usual page formatting that your shop's theme usually applies.
To do this, navigate to the "Themes" section of your Shopify admin (under "Online Store", or by searching for "themes"). Then, under the "Actions" menu for your current theme, click the "Edit code" link.
Next, click "Add a new template".
Then, select the option for creating a "page" template, of type "liquid", and fill in the text box with the name "feed" (or another template name to your liking).
Next, fill in the template contents with the following:
... and click the "Save" button. Your template should look like this:
Navigate to the "Pages" section of the Shopify admin (under "Online Store"), and click the "Add page" button (or search the admin for "add page"). Name the page "Feed" (or another name of your liking), and change the page template to "page.feed.liquid".
Save the page.
Open up the page you just created, and you should see the contents of your feed. :) If you have any questions, head to our community Slack.
Working on getting better at task-writing? See Practicing writing tasks, and Writing a high-quality task.
This very basic task subscribes to shopify/customers/create, and renders an Email action, using an email subject and body taken from user-configured options.
Subscriptions
Code
Export
You can either create a sheet with the sample data shown below or you can use your own data for this tutorial. Keep in mind that the column headers in the first row will be the exact keys that you need to reference in the task when iterating over the data rows for your own usage.
Sharing sheets openly this way on the web so that is accessible by Mechanic works best for non-identifying data. Be sure to clean all customer-specific data and branding from your sheet data before publishing.
From the File / Share menu, choose the Publish to web option.
From the Link tab of the modal dialog that opens, select the sheet you wish to share and the Comma-separated values (.csv) option, and then click the Publish button.
After clicking OK on the confirmation dialog, the modal will update to show you the URL link that you will need to copy into the demonstration task configuration settings. You can safely close this dialog window now.
You can either add the demonstration task using the Try this task button from this task library link - Demonstration task: Fetch data from a shared Google sheet - or you can add it from within the Add task screen inside of Mechanic.
After adding the task you should update the Gsheet URL option field with the link to your sheet that was generated in the prior step. Update the Alert email recipients with one or more email addresses where you want to be notified in case Mechanic is not able to access the shared sheet (e.g. the share is disabled).
Run the task manually using the Run task button and it will run the first sequence of the task, which will make an HTTP request to GET the sheet data.
To see the results of the data retrieval you need to click on the mechanic/actions/perform child event after it appears.
Using the reference information available in these docs, write your own Mechanic script to iterate over the rows of data (array of hashes) that is parsed from the CSV, and make useful updates to your Shopify data using the GraphQL or REST APIs.
If you have any questions, head to our community Slack.
The Flow action accepts at most one resource option, identifying a specific Shopify resource, and resulting in a resource-specific Flow trigger. If no resource option is provided, Mechanic will use the General trigger.
These resource options only accept fully-numeric resource IDs (i.e. 12345). They do not accept global IDs (i.e. gid://shopify/Customer/12345).
customer_id
"Mechanic sent customer data"
product_id
"Mechanic sent product data"
order_id
"Mechanic sent order data"
(when no resource option is given)
"Mechanic sent general data"
This action also sends user-defined data, with one option available for each of Flow's supported datatypes. These options are always sent to Flow, even if they're omitted from the action definition; when omitted, their values are set to the documented default.
user_boolean
Boolean
false
user_number
Number
0
user_string
String
For a detailed review of usage, see Shopify Flow.
password
Optional; a string specifying a password to use for encrypting the file
{% action "files" %}
{
"secure.zip": {
"zip": {
"password": "opensesame",
"files": {
"confirmations.txt": "this data is protected with zipcrypto encryption",
"image.png": {
"url": "https://www.google.com/images/branding/googlelogo/2x/googlelogo_color_272x92dp.png"
},
"receipt.pdf": {
"pdf": {
files
Required; an object specifying a set of filenames mapped to file generators
Mechanic's task library is a central resource for the entire community, and is continually enriched through contributions, via pull requests on GitHub.
You've created a custom task, and you want to share it with the world! This brings us so much joy, and this is what the Mechanic project and this community are all about. If you get stuck along the way, please hop onto the Slack workspace, and we'll be glad to help.
We follow the same process any open-source project does when it comes to code management and code contributions. One bonus of contributing to the Mechanic task library is that once you learn the process here, you'll know how to contribute to open-source projects going forward.
You'll the task library .
Forking means taking a copy of our repository, so that you can make your changes and additions.
Make your changes in your forked repository.
You'll need a GitHub account, you can signup for one .
Visit the and fork it as shown below. You'll make your changes to this copy of the repository.
The task library is made up of the and the supporting documentation. In these next few steps, you'll ensure you can build the , so that you can complete this step when you are ready to submit your contribution.
The Airtable action allows you to create and update tables and records in your Airtable bases.
It provides an authenticated client for HTTP calls to the Airtable API. The various Airtable API methods supported by this integration all share the same top-level structure in the action options.
This integration supports these Airtable API scopes.
Read/Write Records
Read/Write Comments
Read/Write Base Schema
This action requires connecting an Airtable account with the appropriate permissions. To connect an account:
Go to the Settings screen
Click Authentication
Follow the Airtable account connection flow from the Airtable tab
The body of the action response will vary based on which Airtable API method was called. Generally, the response is an object with the following structure (most fields removed for brevity). Running an Airtable action task and reviewing the response is often the best way to see what will be returned in the body.
The PDF file generator accepts an object containing an HTML string, and uses Pdfcrowd to render it as a PDF document. Pdfcrowd employs the Chromium Embedded Framework for HTML rendering, which uses the same foundation as Google Chrome. This allows Mechanic to generate PDFs with modern CSS and JavaScript features, including chart libraries and web fonts.
Option
Description
html
The PDF generator supports all rendering-related options of the Pdfcrowd API, using version 20.10.
For a complete list of options, see .
If it's unclear why something isn't rendering properly, start by testing the HTML being used in a Pdfcrowd playground, at . If the issue is reproducible in the playground, use the "Help" button along the left-hand sidebar to get the ID of your specific playground, and instructions for contacting Pdfcrowd support with the details of your test.
Mechanic-flavored Liquid comes with a complement of Liquid objects, each of which is tied to a resource in the Shopify Admin REST API. Many objects support access to related objects via lookups (e.g. {{ shop.customers[customer_id].orders.first }}); in this way, the REST API can be traversed by resource.
Shopify is deprecating some of the Shopify Admin REST API. The first round of deprecations involve the product and variant endpoints. Read the deprecation notice here.
Our recommendation is to use GraphQL going forward. The product and variant objects will cease to work on on Feb 1, 2025 due to the changes being made by Shopify. It appears that Shopify will gradually phase out the REST API over time.
All of our will be ported to use GraphQL only, which will provide a model for how you can update your custom tasks. You'll be able to update your non-customized library tasks with a click of a button ☺️
Access to these Liquid objects varies, based on the context in which Liquid is rendered. For example, a task that subscribes to shopify/customers/create will have access to the object in its code, via a variable called customer. To learn more about how these objects are made available to task code, see .
Shopify variables in Mechanic do not necessarily contain the same attributes as Liquid variables used in Shopify (in places like themes or email templates) – even if they share the same name.
In Mechanic, Shopify variables always contain data from Shopify events, which are delivered to Mechanic via webhook. This means that Shopify variables always have the same data structure as Shopify webhooks, corresponding to Shopify's REST representation for this data.
For example, while Shopify themes support {{ customer.name }}, Mechanic does not (because does not contain a "name" property). On the other hand, Mechanic supports {{ customer.created_at }}
Each task is given a set of to work with, out of the box. Mechanic's task code editor will tell you which ones are available. For example, for a task responding to a shopify/orders/ event, you might see this:
The , , , and objects are always available for tasks; the object (as in this example) contains the order to which the current event relates.
Webhooks are the nearly ubiquitous carriers of information to and from services across the internet - services like IFTTT, Zapier, Stripe, PayPal, JotForm, and countless more. You can use webhooks to send information from these services into Mechanic, where you can then perform any and you need.
When Mechanic receives data via a webhook, it fires off an event with the user topic of your choice. (For example, if you've set up an IFTTT webhook that sends you tweets, you might choose the Mechanic topic user/ifttt/tweet.) To make use of these events, create one or more tasks that subscribe to this topic. That's it!
The Slack action allows Mechanic to post messages to public and private channels in your Slack instance (as the Mechanic app bot or a customer username).
The Slack action provides a wrapper around HTTP calls to the . The various Slack API methods supported by this integration all share the same top-level structure in the action options.
The Base64 file generator accepts a base64-encoded string, and returns a file containing the decoded value.
This generator is useful when producing images, or other binary content that cannot be represented with a JSON string.
This file generator accepts a base64-encoded string. It does not support any other options.
In Mechanic, an action is an instruction for performing work that has an effect. Actions are generated by , in response to . Each action has a type, specifying the class of operation to be performed, and options, providing specifics about what that operation will do.
Actions are defined by tasks using , which are simple JSON objects specifying an action's type and options. Action objects can be constructed using the .
The Shopify action sends requests to the . Use the to read data; use this action to write or update data.
A typical REST products loop in Mechanic will have the structure below. While this is a concise format to get all products in shop, its main drawback is the inability to limit or filter the number of records and fields returned. This generates a significant amount of extra data for the task to manage in memory during a task run, especially if connected resources are looped as well (e.g. variants).
GraphQL paginated queries work by using the same (potentially filtered) query repeatedly to retrieve resources until the end of the list is reached or the querying is terminated by code logic. In Mechanic, paginated queries are typically implemented by using an outer "for loop", with an arbitrary number of maximum loops (e.g. the 100 in {% for n in (1..100) %}).
Within the query itself, the first filter limits the number of records returned in this batch, and the after filter will instruct which "cursor" the query should start at. This cursor will initially be set to nil, which indicates starting at the beginning, and it will be updated by the looping logic before the next query is run, using {% assign cursor ... %}
{% unless event.preview %}
{% assign customer = customer.reload %}
{% endunless %}{%- assign order_id = order.admin_graphql_api_id | default: "gid://shopify/Order/12345" -%}
{%- capture query -%}
query {
order(id: {{ order_id | json }}) {
id
lineItems(first: 250) {
nodes {
id
product {
title
productType
}
}
}
}
}
{%- endcapture -%}
{%- assign result = query | shopify -%}
{%- assign qualifying_product = nil -%}
{%- for line_item in result.data.order.lineItems.nodes -%}
{%- if line_item.product.productType == "Special" -%}
{% assign qualifying_product = line_item.product -%}
{%- break -%}
{%- endif -%}
{%- endfor -%}
{%- if qualifying_product != blank -%}
Special product notice for {{ qualifying_product.title }}...
{%- endif -%}{%- layout none -%}
{{- shop.metafields.mechanic.feed -}}shopify/customers/create{% action "email" %}
{
"to": {{ options.email_recipient__email_required | json }},
"subject": {{ options.email_subject__required | json }},
"body": {{ options.email_body__multiline_required | newline_to_br | json }},
"from_display_name": {{ shop.name | json }}
}
{% endaction %}{"name":"Customer signup alerts","options":{"email_recipient__email_required":"[email protected]","email_subject__required":"A new customer has signed up: {{ customer.email }}","email_body__multiline_required":"Hi! View this customer's details online:\n\nhttps://{{ shop.domain }}/admin/customers/{{ customer.id }}\n\n-Mechanic"},"script":"{% action \"email\" %}\n {\n \"to\": {{ options.email_recipient__email_required | json }},\n \"subject\": {{ options.email_subject__required | json }},\n \"body\": {{ options.email_body__multiline_required | newline_to_br | json }},\n \"from_display_name\": {{ shop.name | json }}\n }\n{% endaction %}","subscriptions":["shopify/customers/create"],"online_store_javascript":null,"order_status_javascript":null,"docs":null,"subscriptions_template":"shopify/customers/create","shopify_api_version":"2022-04","liquid_profiling":false,"perform_action_runs_in_sequence":false,"halt_action_run_sequence_on_error":false,"preview_event_definitions":[]}{
"zip": {
"files": FILENAMES_AND_FILE_GENERATORS,
"password": PASSWORD
}
}""
user_url
URL
"https://mechanic.invalid/"















This action supports two styles of options: a more verbose nested structure, and a simpler set of positional arguments.
All commands must define a cache key, matching the regular expression /^[a-z0-9_:\-\.\/]+$/i.
In this option style, the cache command is given as the root key of the options object. The root value is itself an option, containing the arguments needed for the selected cache command.
{% action "cache" %}
{
"incr": {
"key": "foo",
"ttl": 600
}
}
{% endaction %}In this option style, the cache command and its arguments are given in a list. Use the cache command reference below to find the argument order required for each command.
Each cache entry is given a default TTL value of 60 days, or 5184000 seconds. (A cache entry's TTL may not exceed 60 days.)
A cache command will always reset the entry's TTL value upon execution, regardless of the TTL's original value.
The required arguments for each command are given below, in the order in which they are supported for positional options.
When a command is given using verbose options, the ttl value (in seconds) is always supported.
Stores a value. Requires key and value. The stored value may be any JSON object.
Using a defined TTL (an expiration interval) given in seconds, stores a value. Requires key, ttl, and value. The stored value may be any JSON object.
Deletes a stored key. Requires key.
Increments a numeric key by 1. Requires key. If the key is not already set, the value before incrementing will be assumed to be 0.
Increments a numeric key by the value of your choice. Requires key, and an integer increment. If the key is not already set, the value before incrementing will be assumed to be 0.
Decrements a numeric key by 1. Requires key. If the key is not already set, the value before incrementing will be assumed to be 0.
Decrements a numeric key by the value of your choice. Requires key, and an integer decrement. If the key is not already set, the value before incrementing will be assumed to be 0.
account
string
Required: the Airtable account to use. Must match one of the Airtable accounts linked in the Mechanic authentication settings.
method
string
Required: the HTTP verb as required by the Airtbale API for the specific method (e.g. "GET", "POST")
url_path
string
Required: the Airtbale API endpoint (e.g. "/v0/meta/bases/AIRTABLE_BASE_ID/tables")
headers
hash
Required: "Content-Type": "application/json"
body
hash
Required: the object that contains a JSON representation of the properties and content of the table, record, or fields being modified
Building the docs requires nodejs and npm. You can install them from here: https://www.npmjs.com/get-npm
While in the project directory, run the following commands to build the docs:
Now that you can build the docs you are ready to contribute!
Your task documentation, options, subscriptions, code, are done in Mechanic. If you choose to use an external editor that's great, you still need to transfer it into Mechanic, so that you can export the task in the JSON format you need for the library. Importing/Exporting tasks from Mechanic is covered here.
If you're changing an existing task you export the JSON, and replace the contents of the task/task_file_name.json and then run the commands npm run build and npm run test.
If you are contributing a new task, you'll export the JSON from Mechanic, and save the JSON file in the tasks/directory of your forked repository, named with an appropriate handle for the task. (For example, a task named "Hide out-of-stock products" should have its JSON export stored in "tasks/hide-out-of-stock-products.json".) And, then you'll execute the commands:
npm run build and npm run test.
If all goes well with the build, you'll see your task listed in the automatically created documentation in docs/README.md
You're now ready to make your pull request! Head over to https://github.com/lightward/mechanic-tasks/pulls and click New pull request, you should see the changes you committed to your fork, and you'll proceed with filling out the pull request form.
After you submit your first pull request, you will be required to read and accept our CLA. The CLA assistant will leave a comment, giving you a statement of agreement that you must paste into a comment of your own.
This process could sound confusing if you haven't done it before, but once you've done it once, it's simple and it is also pretty exciting to go through the process. The other bonus is, you'll be ready to submit a pull request to any open-source software project in the future. If you need help please out to us in the community Slack workspace.

account
string
Required: the Slack account to use. Must match one of the Slack accounts linked in the Mechanic authentication settings.
method
string
Required: the HTTP verb as required by the Slack API for the specific method (e.g. "GET", "POST")
url_path
string
Required: the Slack API method (e.g. "/chat.postMessage")
headers
hash
Required: "Content-Type": "application/json"
body
hash
Required: the object that contains a JSON representation of the properties and content of the message
Currently, these are the only Slack API methods supported by this integration.
This action requires installing the Mechanic Slack app in your Slack account with the appropriate permissions. To install the app:
Go to the Settings screen
Click Authentication
Install the Mechanic Slack app from the Slack tab
The body of the action response will vary based on which Slack API method is called. Generally, the response is an object with the following structure (most fields removed for brevity). Running a Slack action task and reviewing the response is often the best way to see what will be returned in the body.
Finally, the query filter of a resources query gives the ability to drastically reduce the number of records returned, allowing for very targeted inclusion and exclusion rules (e.g. products having a certain tag). Each resource has its own list of query filters, which can be reviewed in the GraphQL Admin API docs
If a query has the potential to return a very large number of resources (including connected resources) in a shop, then a bulk operation query may be better suited than using paginated GraphQL queries.
To see a code diff from a Mechanic library task that was recently converted in this manner, click here.
{% action "cache", "incr", "foo" %}{% action "cache", "setex", "foo", 5, "bar" %}{% action "cache" %}
{
"set": {
"key": "foo",
"value": 5
}
}
{% endaction %}{% action "cache", "set", "foo", 5 %}{% action "cache" %}
{
"setex": {
"key": "foo",
"ttl": 60,
"value": 5
}
}
{% endaction %}{% action "cache", "setex", "foo", 60, 5 %}{% action "cache" %}
{
"del": {
"key": "foo"
}
}
{% endaction %}{% action "cache", "del", "foo" %}{% action "airtable" %}
{
"account": "AIRTABLE_ACCOUNT_NAME",
"method": "POST",
"url_path": "/v0/meta/bases/AIRTABLE_BASE_ID/tables",
"headers": {
"Content-Type": "application/json"
},
"body": {
"name": "Example Checklist",
"fields": [
{
"name": "TODO",
"type": "singleLineText"
},
{
"name": "Complete",
"type": "checkbox",
"options": {
"color": "greenBright",
"icon": "check"
}
}
]
}
}
{% endaction %}{% action "airtable" %}
{
"account": "AIRTABLE_ACCOUNT_NAME",
"method": "POST",
"url_path": "/v0/meta/bases/AIRTABLE_BASE_ID/AIRTABLE_TABLE_ID",
"headers": {
"Content-Type": "application/json"
},
"body": {
"records": [
{
"fields": {
"TODO": "Review Mechanic",
"Complete": false
}
}
]
}
}
{% endaction %}{
"type": "airtable",
"run": {
"ok": true,
"result": {
"status": 200,
"body": {
...
}
}
}
}npm install # install dependencies
npm run build # compile docs
npm run test # apply sanity checks{% action "slack" %}
{
"account": "SLACK_ACCOUNT_NAME",
"method": "POST",
"url_path": "/chat.postMessage",
"headers": {
"Content-Type": "application/json"
},
"body": {
"channel": "CHANNEL_ID",
"text": "Slack Example Message",
"blocks": [
{
"type": "section",
"text": {
"type": "mrkdwn",
"text": "Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet consectetur adipiscing elit."
}
}
]
}
}
{% endaction %}{% action "slack" %}
{
"account": "SLACK_ACCOUNT_NAME",
"method": "POST",
"url_path": "/chat.postMessage",
"headers": {
"Content-Type": "application/json"
},
"body": {
"username": "AiRobot",
"icon_emoji": ":robot_face:",
"channel": "CHANNEL_ID",
"text": "Slack Example Message",
"blocks": [
{
"type": "section",
"text": {
"type": "mrkdwn",
"text": "Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet consectetur adipiscing elit."
}
}
]
}
}
{% endaction %}{
"type": "slack",
"run": {
"ok": true,
"result": {
"status": 200,
"body": {
...
}
}
}
}{% for product in shop.products %}
{% comment %}
-- product processing here, using REST fields
{% endcomment %}
{% for variant in product.variants %}
{% comment %}
-- variant processing here, using REST fields
{% endcomment %}
{% endfor %}
{% endfor %}{% assign cursor = nil %}
{% assign search_query = nil %}
{% for n in (1..100) %}
{% capture query %}
query {
products(
first: 250
after: {{ cursor | json }}
query: {{ search_query | json }}
) {
pageInfo {
hasNextPage
endCursor
}
nodes {
id
# relevant product fields
variants(first: 100) {
nodes {
id
# relevant variant fields
}
}
}
}
}
{% endcapture %}
{% assign result = query | shopify %}
{% if event.preview %}
{% capture result_json %}
{
"data": {
"products": {
"nodes": [
{
"id": "gid://shopify/Product/1234567890",
"variants": {
"nodes": [
{
"id": "gid://shopify/ProductVariant/1234567890"
}
]
}
}
]
}
}
}
{% endcapture %}
{% assign result = result_json | parse_json %}
{% endif %}
{% for product in result.data.products.nodes %}
{% comment %}
-- product processing here, using GraphQL fields from the query
{% endcomment %}
{% for variant in product.variants.nodes %}
{% comment %}
-- variant processing here, using GraphQL fields from the query
{% endcomment %}
{% endfor %}
{% endfor %}
{% comment %}
-- if there is another page of data, then update the cursor for the next loop
{% endcomment %}
{% if result.data.products.pageInfo.hasNextPage %}
{% assign cursor = result.data.products.pageInfo.endCursor %}
{% else %}
{% break %}
{% endif %}
{% endfor %}Start by opening Mechanic, from the "Apps" section of Shopify. Once in Mechanic, click the "Settings" button in the upper-right corner, then navigate to the "Webhooks" tab.
Webhooks should be named after the service that will be sending you data, with an event topic that makes sense, using the format user/subject/verb.
For this example, we'll simply call ours "Example", with an event topic of "user/webhook/test".
Click the submit button to save the webhook, and use the copy button to copy the resulting webhook URL.
The URL will look something like this:
Back on the Mechanic homepage, click the "Add task" link.
Then, click the "Start a blank task" button.
Keeping things simple for this example, we'll title the task "Webhook test", with a subscription to "user/webhook/text" (to match the webhook configuration), and a simple Echo action in the task code.
Lastly, save the task.
Open https://reqbin.com/, and construct a request to our webhook. Here, we'll select "POST", paste in the webhook URL, and fill in a simple piece of content. (Webhooks support plain text, form-encoded content, and JSON; for this example, we'll use JSON.)
Click the "Send" button, and you'll see a 204 response returned within ReqBin.
Over in Mechanic, watch for the new event on the "Events" page (or in the "Recent events" section of the Mechanic homepage):
Click on that event to see the results of our task and its echo action.
This last part is up to you! Provide the webhook URL, generated by Mechanic, to whatever service you'd like to use. When provided with this URL, the service will start sending your data over to Mechanic for processing.
That's it! :) Adjust to taste.
{% action "files" %}
{
"image_from_base64.jpg": {
"base64": "iVBORw0KGgoAAAANSUhEUgAAAC8AAAAuCAIAAAA3GddeAAAAAXNSR0IArs4c6QAAAMZlWElmTU0AKgAAAAgABgESAAMAAAABAAEAAAEaAAUAAAABAAAAVgEbAAUAAAABAAAAXgEoAAMAAAABAAIAAAExAAIAAAAVAAAAZodpAAQAAAABAAAAfAAAAAAAAABIAAAAAQAAAEgAAAABUGl4ZWxtYXRvciBQcm8gMi4wLjUAAAAEkAQAAgAAABQAAACyoAEAAwAAAAEAAQAAoAIABAAAAAEAAAAvoAMABAAAAAEAAAAuAAAAADIwMjE6MDI6MTMgMDA6MjQ6MjMAdW0xkQAAAAlwSFlzAAALEwAACxMBAJqcGAAAA6ZpVFh0WE1MOmNvbS5hZG9iZS54bXAAAAAAADx4OnhtcG1ldGEgeG1sbnM6eD0iYWRvYmU6bnM6bWV0YS8iIHg6eG1wdGs9IlhNUCBDb3JlIDYuMC4wIj4KICAgPHJkZjpSREYgeG1sbnM6cmRmPSJodHRwOi8vd3d3LnczLm9yZy8xOTk5LzAyLzIyLXJkZi1zeW50YXgtbnMjIj4KICAgICAgPHJkZjpEZXNjcmlwdGlvbiByZGY6YWJvdXQ9IiIKICAgICAgICAgICAgeG1sbnM6dGlmZj0iaHR0cDovL25zLmFkb2JlLmNvbS90aWZmLzEuMC8iCiAgICAgICAgICAgIHhtbG5zOmV4aWY9Imh0dHA6Ly9ucy5hZG9iZS5jb20vZXhpZi8xLjAvIgogICAgICAgICAgICB4bWxuczp4bXA9Imh0dHA6Ly9ucy5hZG9iZS5jb20veGFwLzEuMC8iPgogICAgICAgICA8dGlmZjpZUmVzb2x1dGlvbj43MjAwMDAvMTAwMDA8L3RpZmY6WVJlc29sdXRpb24+CiAgICAgICAgIDx0aWZmOlhSZXNvbHV0aW9uPjcyMDAwMC8xMDAwMDwvdGlmZjpYUmVzb2x1dGlvbj4KICAgICAgICAgPHRpZmY6UmVzb2x1dGlvblVuaXQ+MjwvdGlmZjpSZXNvbHV0aW9uVW5pdD4KICAgICAgICAgPHRpZmY6T3JpZW50YXRpb24+MTwvdGlmZjpPcmllbnRhdGlvbj4KICAgICAgICAgPGV4aWY6UGl4ZWxZRGltZW5zaW9uPjQ2PC9leGlmOlBpeGVsWURpbWVuc2lvbj4KICAgICAgICAgPGV4aWY6UGl4ZWxYRGltZW5zaW9uPjQ3PC9leGlmOlBpeGVsWERpbWVuc2lvbj4KICAgICAgICAgPHhtcDpNZXRhZGF0YURhdGU+MjAyMS0wMi0xM1QwMDoyNTozMlo8L3htcDpNZXRhZGF0YURhdGU+CiAgICAgICAgIDx4bXA6Q3JlYXRlRGF0ZT4yMDIxLTAyLTEzVDAwOjI0OjIzWjwveG1wOkNyZWF0ZURhdGU+CiAgICAgICAgIDx4bXA6Q3JlYXRvclRvb2w+UGl4ZWxtYXRvciBQcm8gMi4wLjU8L3htcDpDcmVhdG9yVG9vbD4KICAgICAgPC9yZGY6RGVzY3JpcHRpb24+CiAgIDwvcmRmOlJERj4KPC94OnhtcG1ldGE+Ci1W4c0AAA3XSURBVFgJvZgLlBTVmcfvraquqn5Uv3t63swwvAaQhyBCFEUhWSIgKJrVaBLMakjMaszRzWp213PUPScn8WCOiWZfybpn17hZ4yMcgkogQRAIEeMwwwwzTGaaGaZ7evpR1V3vd929zfCKYCKIqalTdaf6Vt1f/b/vft93CyKEwF92mxwRD4v/IIB4eIgbkIAQUH8xEtd1MYGoqNnx0gQviZolmZ6DSB9FMK7d2V63YE47/KS1QZ7nep6uKAd+e3DCIL26GQbB8aIhqYaHgJ9lY9GQI0t7tr7x2H03foLa4PfEevDlcm/vEcmwIqnGkCTnxNKITY0Jmmu7sbA/GAgwrE8uGSqk9nRnPikarIdUrRw90qs5Xrx5mqdbuUIJ09GVYVvIOOwsKhCLxsLJOEN5riRJuod4zbn8NFgS27KO9fYUe/rS+SIcHFaFSiQZLyxamudCFEnNTaNGd7wST6Xr2VSMtDWEIFIcD3vwZaaxXUcoFo+/s4/evoPv7n61UBzUdSBW7qfoldnRHWs2GO2t8UikI0CpThbE6Za6eEkhVcvBTp0IMZeTxrSszOiIuWMn8drWN3304IpV42I1mxk+NpLpEip7+/oWRaK9M/8mEg1Hg35WUxPW0RTRyXuxYlVRda0xGbxsNLqm9Q0PE4d+X319667m1lLHjInenpH+o6VigZIlwTGPREI3TORiJJmMheMB1vDBplhjodDff2JKviS6ut6WDl8eGlVRuvuOQt20f7F1pz+UiSXHDuwfGTpWEQRHV13bhJ4bmDOb7JwRi3FxLhhnGH8sAiBhT3BH3n6jUCDrOaKzrZH4+NFPqlb7eo9QiQbY1d2Tyx1FoLe7+w/H+gWet3XVcy3kua0U3UmRTnNLvC4VphkCeLph5Eu57EQpaefc0uDSzob6VPTj0miqMtDfJxpOvijoY2OQZU9MFMZOjEhi1TFU5Fg49gUI4t5INH3wXTkQCkXCELi6rZXF0nBmZGBwCJKgzs6sWjwdR+qPZSnL8Y4ODEyUymRiytDo2NyqNK0qRqqyqaqWrgLHwpG+EYKNtP8BwzCvW06uWkGSSFWrkiwXiuXR0Wy5zOdGs/UR6qZrr/hYeUoXxYFMNqMiQAbzx4+XNOuIR6xy0bcp8JJnHsa+AlAHQHcQ5AbbUzo7+Ucf4RpSmlQRxaogVPKFMt4qvFAu8UuWX5+IRy893khDQ++/+tpxLtlx35e7fn2kwGcJCvQ3T/XaJm4sZ//eVIuKGEZgBkVRyVRh8eLKI98ML5hriIJYxZtU4rF/YxK+zAs47N1960aIlbmE6OeaZvW9Q13PPNNblNgnfvh+n5FRQjpRRxaPEIFg//KVQu54c6ouJlfTPrqnvh7deAO3dnUkHDL5iWqlIklqpSoKlSqPWUp8qVS+/dbbprZNmZxMH+o3nuPYqkoFgwRJ4q4eTsWGbubGlXf2Dv/ouf5sceiuh5vDU0d6h0tVRTJCpBFtI/XW5nq6s8MNrHODrJmIhNPJZMhPq5JaHMcGEiVFFJUaDTZQGaMIsVjyjttOCfOh2iDblrZtBcf+QKaSyO93cU1kGk6hwL+9Rzq4f8xxD0xbEpz9qbHhMTxFFdMyEUmEp+fN0TpDb6GTiXAwGeNi4WDAs5GgiKokYQpZFWUFE9VsVBNGkCTl0Ye/GgoFJ4X5UBplz2/Q4/8YE0Sg6bptYWWok3WaAdAJ5B1iwtmORVMJ/9jICUkzHRzFcMUU4FT/zLwxOs3hKY8lkd8HbEvHEUCWFTyHNFnRREmqVKqlmoH4iWJp+bJrVq5YTsCzUeYCljL27hGffLK5yANNBbbtdxw/AiYAPIRjPjIDicP+lB5Ojxd5QVJcQOLqjSZJhkTRWBL6EhZ812ceZrzZrhlTagQqTkKKakiSjG2EVTlpIz4WS9x7z5cgcRblAtpYPYetpx4PZjLAVIFrI89xCWAhoABQgrV9GNKj/gTnkkVR9jxEUaSPJFmaigbZdMiXrquzyGCI3toaPFpUm3keSLKjGmbNTBJGqdmoXBZwDfHA5q80NTZMTqULW8oaHXG2fAceHySwFqQDKBej4BmIaUQEBIB4hAaooM0lbToIMApB0D4ywPgiQbYxxtUnw+EIhdz67tJVSHzNB3mp2s5LHpZGwR5TxfOoUuYrmqrfe8+ma69ZSvyxMH+kDVJU+4XnggN785yb9tvAjxDOMA5wbKC6QHCA6IBxjxz2J5lUCxWJkyRGoTiWiYcD9YlQSyrMhJjA2LAiFI8psE/pmEJ0UaRrgYgoy9hhxarE45ktSretv+X2Detx2XVGkjON05cQ0v5jS/D4y9Z0M6whAq8uNOSZwDWBaQLBqO2SDoeNoBhpapoyLRTFVRwZDvpTUa4uxiWiIQvo9PZXPv3icwc75v520aqiy3YrnSjf3cplfHQQuzCOwbblPPT1+29Zt5Y8GTXOQJxpnKIx3tnNFF4BHZ5XdVkHL3RspLuugVMtQC5w8FEFRhllDIaJ1SebGiKRIDYQViXOBTg/qUoF+o3/Xbn9pQlA74635DXLNGQ82xSvrjw61MBUAcAFKnzwa19dv+azH4aCmWo0niSj/d+nZslAcykWkYgENgAGIDCNRStNn07NWcEoRqlrzNqVSTWlW5vSYY4LsTTHUAQ0J04MCr/55eZfvSr7ueev/EwPV+9VRRunSdO0sH1Bsjp+bE57cvOmuzes+SxOFWeUOL9R+03b9XKg/RBgAfLbRADTUcBioekh09WpBem7nvUlGk/s/52Y743NZJMds1obkgwBKeCYSik/1Jvfte3a6jg3fdb3mJYDbJyoVBzLsm3HclzTsnVNX71s2YNfvPnqRQv/NAomoayREUp/lrjSBDqEtgstAEwPKBTQ/cCizI7HuPjUf3vhv7f//KcIEnmTnb9iTcJPKVW+WBzPHT4o7Hlzjiqsvf66f3VjOyouEEXoeXgaqh4yTJuzlIduX/WljX81vb3lfCXOv0KZwzsCy2wvuAR5cUcPWLLgZ2wIcYB15fyi9JI1g8cGfvLcD13OVwVJcbT/dztfZ1auLo70Fw7uM4+8m66Ub0nGy9nyzyAlewRlOQ4kZBexmrJam/jCt75+w603RSPh8we+4BXKv+AzZAyjhCBkfB5F2CZBupBEgEBcS52P9hGF3SuWWz/uvTLKmKEw+/7ebWJuqFES6KGjrGlcTdPNJPXUhJwNx0IEiR2eNfV5Kv95MTv/a5sWbryJDn9UFMxHUYl2fJrMFbgoJHxnodVcF1n+wdT52XsaWrqeVrMZbfE1n5L5UveuX6U0g3LsBkBd5wv0+rhtLt1Ynmgx5FlGdYktX28b8IpZ9bdvvCiUGs3Zwc9pWZrK7342MnOInmlRkaZOLrDlQbwyCemgQzDkDtOIOnZzhLxlKRNhfW/9WprvVJe5+ixkT0dOGnkNCOTWr2dmzDjnkR+peSEaz60e+kk8+RIz9UbgxoDNUMhZOAfGYs6L/7Lv/e17E6aTIoi1Abh4Stuhtqktv3xzletOIVEE4HlZ2yskwc2bxwbPlgofieV8bVzHKRzelRSfp+e3ARQCLgeAD6A8pOOUKmp794WFSh1FfG4eMXdaM3/vMy3ZPMlsa9ABU+sHav6GQ0TA749GP5ARPwrQ6YSOkCzkygNv4Szp9v8D3VwGTCtuApgAMALo4Pig+j9/+wv5PWF2ANy1iZ13TyN66KnUwpVjo+N1QRjApTrAfn/yCAFB4ix0IdX/HNGpe3AuIA1e79+Xyww3hLtRFC88NODSgJABVaerjQd+/PPht8fqI8TabycW33wVTG2pwLp//8536372n7OkmiCTqhD40xke0rZcyzpnPvw5itO/n3kDSPhTnr+lgX+MaPaAPwk8XEGwgOpAIJjZe2j/j/bXp8i7n5/afn2bJP9TLmPtfPq+pX37p5/ga7EJnqLBj8VfPsKa7pRKp4e4iPMpGvxCyLIYc5ReSKHo1TXFIQdgDNCWMmHu/O5/+UP2ff93VXpeR2n45oaF88HYM5vsN4K4IsZZFZvGq0lychECsNWk2XOYjmkXQXG662m/gdC1Hd/4bsBGYCAOXPz4IKChbRx875UXdC33wK7FjQupyuC8his24CDHhWCi3gIsgj5AYpqTKFiVEAIT626mXvwpvWDB6SEu4nxKG1uTlC231SV6HQGHYhqm5wCS8ign18Vne3s2vzw7wkqV7rXxhZsphsHFIGRjAK9tWJf0gcn6EH9pxQlX/Nxfx554kpk+/ZRQF0FS63qKhvTRxrQkcfUUTx2HrU3AqABhyPbVa4q9/omE3y0U37szvfpxAhegeO4AGnDYySBigIlTOcT/1x5kfeOhwMOP+BobLw3lLA0uUWmkAZpEWcsb+T0CjN1TpqmB2XPicjcoiBsjq/5uEqX2CnijA26AgqzDsICjMJPf/f4PQnfcQeCIN+k+k90u8nhSG4SKPfsb5C47F3D7PVCRfC1Bs0yPg9W+5htCM69tbJhJ0DjGnto8XLnrRQoi6Ac+PyhNabW/9c+Nn78TJ73TXS7xXLu/ViQaJbgcUjBAzDBhiCoOrYt85emoIfJHX0+3zvvg63qGp+QpktCCAeGmO8ObH022teN11SUinHPbpDZetfewRdxKzFhNpVTIcPEvrqMCIZ+TYOMPfBAF03uWLYuyNcu6/3tN16zAHJeQBM5hONusfdlHjlM++FZ8yUrSd9ocf9L2nmtq+UGko9A0/AmoFnsv1/b/1t5SZGHoKlMAAAAASUVORK5CYII="
If you don't need the follow-up event for a particular action, add __perform_event: false to that action to skip emitting mechanic/actions/perform while still performing the action.
To attach meta while using any of the action tag syntaxes, add __meta and Mechanic will move that value into the action's meta field.
Learn more: Responding to action results
An action type determines the class of operation to be performed. While actions may vary greatly, there are only a few action types. Shopify is treated as a first-class action because it's the primary API Mechanic automates against.
Performing operations on the store's Mechanic cache
Debugging; displays the options that it is provided, with no side-effects
Sending transactional email
Generating custom user events
Generating files of various types, storing them at a temporary Mechanic-provided URL
Performing FTP file uploads and downloads
Mechanic also maintains a set of integration actions for third-party services beyond Shopify.
Airtable
Create and edit tables and records in Airtable
Shopify Flow
Sending customer, order, product, and general triggers to Shopify Flow
Google (Drive and Google Sheets)
Advanced integration with the Google Drive and Sheets APIs
Google Drive
This action has several usage styles, each with a different set of constraints on action options.
This usage style invokes the Shopify GraphQL Admin API. In this style, a single GraphQL query string is supplied as the action options. The action tag has specific support for this action type, allowing this string to be provided as the contents of an action block.
{% action "shopify" %}
mutation {
customerCreate(
input: {
email: "[email protected]"
}
) {
customer {
id
}
userErrors {
field
message
This usage style invokes the Shopify GraphQL Admin API, and supports combining GraphQL queries with GraphQL variables. This can be useful for re-using queries with multiple inputs, and is critical when dealing with very large pieces of input. Because GraphQL queries (excluding whitespace) are limited in length to 50k characters, GraphQL variables can be used in cases when large inputs (like Base64-encoded images) need to be submitted.
query
Required; a string containing a GraphQL query
variables
Required; a JSON object mapping variable names to values
This example shows how the query and variables may be built up separately, and provided to the action using concise tag syntax.
Required; a string containing the HTML, CSS and JavaScript to be rendered
...
Additional Pdfcrowd API options supported; see below
During task preview, Mechanic scans the task's subscriptions. For each event topic found, Mechanic constructs a synthetic preview event, resembling one that the task might encounter during live use.
By default, each preview event's data is sampled from previous events that the Mechanic account has seen, for the same topic.
However, developers may define their own preview events, containing whatever data the developer wishes to use for preview. This may be useful for several reasons:
Most tasks conditionally respond to events based on their data. Controlling the event data present during preview allows the developer to deterministically verify the results of the action.
Further, by deterministically/predictably generating actions, the developer can consistently demonstrate the permissions they need to Mechanic. (To learn more about this, see .)
Defining preview event data is usually simpler than defining .
Stubbing the event variable (or any of the ) removes any intelligence from the objects Mechanic generates from event data, a drawback avoided by defining a preview event and its data. Using the as an example, a task may typically access its custom attributes via order.note_attributes.color, or via order.note_attributes[0].value. This dynamic behavior is lost if the event variable is stubbed out, which can result in behaviors that are difficult to diagnose.
Multiple preview events may be defined per event topic. This allows developers to verify that their task renders the appropriate results under a variety of circumstances.
Defined preview events can be labeled with a description, which is visible in the task preview pane. This makes it easy to identify the scenario that a preview event is meant to represent.
Preview events may be defined using the "Edit preview events" button, in the task preview pane.
The configuration area for preview events contains a quickstart link for each event topic the task subscribes to, allowing developers to get started using sample data if the event topic is known to Mechanic. Or, the developer may start with a blank preview event definition, filling in whatever topic and data are useful.
A developer may define any number of preview events per topic. If no preview events are defined for a given topic, Mechanic will construct its own ad-hoc event during preview.
Displayed beneath the event topic in the preview pane, allowing the developer to distinguish one scenario from another.
Identifies the event definition to Mechanic, when Mechanic goes to construct preview events by topic.
Used to construct event.data, and may be set to whatever values are useful in representing a specific scenario. The data structures used here should resemble what Mechanic will receive for a live event of the same topic.
Notably, the data here can be limited to just the properties that are useful. For example, while Mechanic might normally generate a complete payload for shopify/orders/create, the developer might only care about the "email" property of the order – and so their defined preview event data might be limited to just that property. (Note that the inverse may not be true: defining preview event data for traversals into other objects, e.g. using preview event data to define a value for order.line_items[0].product.title, will not work.)
For a trivial task, subscribing to shopify/customers/create, and having the following task code...
... we define two preview events, one which represents a Gmail user, and one which does not. This allows us to easily assert that the task behaves properly in both scenarios.
Preview event definitions are stored along with the task itself, and thus are present in the tasks version history (and, naturally, in task exports).
Because definitions are a part of the task itself, they're appropriate for use as a testing tool, allowing the developer to verify that a task behaves as intended at every stage of the task's development.
The Google Drive action allows you to upload files to your Google Drive.
It supports various file types and can generate files dynamically using file generators, including text files, PDFs, CSVs, and HTML files. Mechanic interacts with Google Drive via the Google Drive API, using OAuth2 for authentication. \
The uploads hash supports these properties:
This action requires connecting a Google account with the appropriate Drive permissions. To connect an account:
Go to the Settings screen
Click Authentication
Follow the Google account connection flow
Files can be organized in folders by including path information in the filename:
Use forward slashes to separate folder names (e.g., "reports/2024/monthly/file.pdf")
Folders will be created automatically if they don't exist
Can only access folders created by this integration
Invalid characters not allowed: < > : " / \ | ? *
The action returns details about the uploaded files. The response is an object with the following structure:
The Google action allows you to interact directly with the Google Drive and Sheets APIs, and is a more advanced integration type than the streamlined Google Drive and Google Sheetsactions. The advantage is that it allows use to use any of the features in the Google Drive, Sheets, and Docs REST API. Mechanic interacts with Google using OAuth2 for authentication.
Utilizing the Google action beyond the demonstration tasks requires reviewing and comprehending the Google Drive API reference docs. The Mechanic team will not be able to provide developer assistance with this API.
The Google action provides a wrapper around HTTP calls to the Google APIs. The various Google API endpoints supported by this integration all share the same top-level structure in the action options.
This action requires connecting a Google account with the appropriate Drive permissions. To connect an account:
Go to the Settings screen
Click Authentication
Follow the Google account connection flow from the Google tab
The body of the action response will vary based on which API endpoint is called. Generally, the response is an object with the following structure (most fields removed for brevity). Running a Google action task and reviewing the response is often the best way to see what will be returned in the body.
The Files action evaluates its options using file generators, temporarily storing the resulting files and making them available via a randomized Mechanic URL.
This action is most useful in concert with mechanic/actions/perform, by which a task may take the resulting file URLs and pass them on to another service. Used by itself, this action can also be useful for quickly testing file generators.
This action accepts a JSON object, whose keys are filenames and whose values are file generators. In this way, many files may be defined and generated by a single Files action.
A Files action returns an object having the same keys (i.e. filenames) as its input. Each value is an object, having the following properties:
This task generates a variety of files. It then re-invokes itself (via mechanic/actions/perform), sending an email containing links to each of the generated files.
Subscriptions
Code
At its core, accessing a single resource via either API is effectively the same. Typically this involves passing the ID of the resource to the API and getting back the data for that resource.
{% assign product = shop.products[product_id] %}In a REST call, every field of that resource will be returned, allowing the usage of simple dot notation to utilize whichever fields are desired without first requesting them.
The equivalent query in GraphQL would need to be augmented to include the desired fields.
Occasionally, the REST and GraphQL APIs do not use the same field names. And in some cases, there are some fields with no counterpart between the APIs. Review the API docs in detail for the resource being queried to make sure the task code is using the correct field names.
This is a basic task to check a product's status, type, and tags, and then output a log entry if that product qualifies.
The preview block is only showing the fields from the REST product webhook that will be used in the task. In reality, there are about 150+ lines of detail from a product webhook which has only a single variant and image. This grows much larger as variants and images are added to the product.
The product id used in the GraphQL query below comes from the REST-like product webhook, which will still exist after the REST product endpoint deprecation.
The preview block simulates the relevant shape of the returned data, which typically matches exactly what was requested in the query. This could vary though based on the task logic following the preview block.
To see a code diff from a Mechanic library task that was recently converted in this manner, click , and review the code variations between the {% if event.topic == "shopify/orders/create" %} blocks.
Tasks may use the shopify Liquid filter to convert GraphQL query strings into simple result objects, by sending the query to the Shopify GraphQL Admin API. The easiest way to build these queries is via the Shopify Admin API GraphiQL explorer, which allows queries to be interactively constructed.
The accepts a GraphQL query string, and returns everything back from Shopify's GraphQL admin API. This means that reading back GraphQL data is as easy as this:
If you're working with multiple pages of data, you might use set up a forloop, using a cursor to retrieve page after page:
The hardest part of using GraphQL in Mechanic is writing the query itself. :) For help with this, we recommend installing . It provides an environment where, using auto-complete and built-in documentation, you can rapidly build the right query for your task.
Note: GraphQL queries (excluding whitespace) are limited to 50,000 characters. That's a hard limit, enforced on Shopify's end – if you bump up against it, you'll need to adjust your query strategy to always stay under that limit. If you're saving large values to a metafield, for example, consider separating those values using GraphQL variables, keeping the query itself trim. Learn more about this scenario using the , or with the .
... you want to make things more efficient. GraphQL is fantastic for being really precise about what data you want, which makes your tasks run in less time: no more looping through collections to find your data, and no more downloading data you don't require.
... it's easier and more readable to use Liquid objects, unless performance becomes an issue. Ultimately, the most important thing is that your task works well tomorrow – and that includes making sure that whoever works on it next understands what you're doing. If that means using a quick-and-simple Liquid lookup over a moderately-more-complex GraphQL lookup, go for it.
... you find yourself staring at nested loops. Looping through all orders is one thing – it's quite another to loop through pages of orders and loop through pages of line items within each order. For those scenarios, whenever possible, use a bulk operation.
File generators are invoked by actions to create new files, using options provided by the action, and handing the resulting file back to the action for further use. In this way, tasks can make choices about what files to generate, and what to do with the results.
Decodes base64-encoded content, returning a file containing the results
Renders HTML using a full Webkit browser, returning a PDF file of the results
Allows defining file contents using a plain string, instead of a file generator object
Generated files may each be a maximum of 20MB.
File generator objects, like , are plain JSON objects each having a single key, and a single value. The object key specifies which file generator is to be invoked; the object value contains the options used for that generator.
In practice, file generator objects are given as values in a larger JSON object, in which filenames are mapped to file generators.
In the following example, a action is defined, mapping filenames ("invoice.pdf", "external.jpg", and plain.txt) to file generators (a PDF generator, a URL generator, and – implicitly – a plaintext generator). Note how the file generator invocation varies, based on the specific file generator in play.
These are the Mechanic actions that support file generators.
Events, tasks, and actions are all processed using queues, in which a piece of work is enqueued, and performed in its turn. Each piece of work is called a run. Thus, Mechanic performs work using event runs, task runs, and action runs.
When performed, a run has a result. Depending on the type of run, this result may define additional runs to be performed after it concludes.
Event runs, when performed, may result in a set of enqueued task runs.
Task runs, when performed, may result in a set of enqueued action runs.
Action runs, when performed, have behaviors that vary by .
If the originating task , each action run will spawn a new event containing that action's results. This new event will be processed in an enqueued event run, creating an opportunity for the task to respond to the action's results.
Most runs are scheduled to be performed immediately. Some runs may be for the future. Some runs may be , once performed.
At the moment a run is performed, it loads in all related data (which may include the related store, or the related event, or the related task).
A normal flow in Mechanic looks like this:
An event is created – possibly by a , or by a , by the , or by an .
An event run is created, and performed. During this phase, Mechanic scans the store's tasks to see which ones are relevant for the current event, by checking the subscriptions on file for each task. For each task that Mechanic discovers for the event, a task run is created. (If the task subscription involved an , as in mechanic/scheduler/daily+2.hours, the task run will be set to wait for that amount of time.) The result of the event run is this set of task runs.
Each task run is performed. During this phase, Mechanic takes each task's , and renders it using the associated event. The result of the task run is the set of JSON
Understanding this sequence of events is important. Task runs do not come into existence until the event run has been performed, and action runs are only performed after their task run has fully concluded.
Critically, this means that tasks do not have direct access to the effects of the actions they generate. Actions are performed later in the sequence, and their effects will only be seen by subsequent task runs.
In general, given a mix of event, task, and action runs that are all due, Mechanic will perform due action runs first, then due task runs, and finally due event runs.
If Shopify's rate limit for either the GraphQL or REST Admin API has been reached, Mechanic will skip over task runs and over runs, until both rate limits have been recovered. In these cases, Mechanic may choose to perform due runs of a lower priority, while it waits for the Shopify API rate limits to recover sufficiently to perform the higher priority runs.
Mechanic supports Shopify's bulk operations GraphQL API, allows developers to submit a query to Shopify for asynchronous processing, and making the results available to the task once complete.
This approach dodges the issues inherent in synchronous methods of reading data (like GraphQL via the shopify filter, or REST via Liquid objects). Unlike these methods, the bulk operations API does not exhaust Shopify API limit for your Mechanic account, and therefore does not slow down other tasks. It also does not require any special logic for pagination, since Shopify handles all data collection.
Shopify only permits apps to run a single bulk operation at a time, per store. Actions that create another bulk operation, while one is already running, will return an error.
This area deserves improvement! To discuss the future of this behavior, visit the related feature request:
Use the action to execute a bulkOperationRunQuery mutation (see ). Mechanic will detect this mutation, and will begin monitoring the bulk operation in progress.
Add a to mechanic/shopify/bulk_operation.
Once Mechanic detects that the bulk operation has been completed, the platform will automatically re-invoked the same task with an event having the topic "mechanic/shopify/bulk_operation", containing the bulk operation's data, when the bulk operation is complete. (As with , Mechanic will only invoke the current task when the bulk operation completes; no other task will be notified.)
When processing a mechanic/shopify/bulk_operation event, the task will have access to an called bulkOperation, containing all attributes of the bulk operation ().
The set of objects returned by the bulk operation is made available as bulkOperation.objects, allowing you to scan returned data immediately, using an expression like {% for object in bulkOperation.objects %}
.
In most cases, every object that has an ID will appear as a separate object, in the same set of objects. For example, if a product and five variants are returned, there will be six objects returned – the variants are not nested inside of the product object.
The JSON objects returned from bulk operation queries each include a "__parentId" attribute for connected objects, containing the parent object's ID. To make managing task scripts easier, Mechanic allows you to simply call {{ object.__parent }} to look up an object's parent.
Subscriptions
Code
... your task needs to collect and process a lot of data. Tasks responding to bulk operations operate with a higher memory allowance than other tasks, decreasing the chances of your task being terminated for memory exhaustion.
... paginating for data would be too complicated. Pagination in GraphQL can be tricky when using nested resources.
... you only need a little bit of data. Use the filter instead.
... you're responding to a Shopify event, and the data you need comes along with the event data. Use instead.
An action object defines work to be performed by an , after the task is fully finished rendering. Action objects are most easily generated using the .
An action object is a plain JSON object, having the following structure:
Shopify allows apps to inject JavaScript into the online storefront. (This is facilitated by in the Shopify API.)
Mechanic supports this by allowing each task to specify its own JavaScript, to be injected into the online storefront.
Here, the developer can add in their own JavaScript code, taking advantage of Liquid for mixing in data from the current store, or from the current task's options.
https://webhooks.mechanic.dev/00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000{
"base64": BASE64_ENCODED_VALUE
}{% capture query %}
mutation DeleteProduct($productId: ID!) {
productDelete(
input: {
id: $productId
}
) {
userErrors {
field
message
}
}
}
{% endcapture %}
{% action "shopify" %}
{
"query": {{ query | json }},
"variables": {
"productId": "gid://shopify/Product/1234567890"
}
}
{% endaction %}{% assign metafield_owner_id = "gid://shopify/Customer/507332001849" %}
{% assign metafield_value = hash %}
{% assign metafield_value["foo"] = "bar" %}
{% capture query %}
mutation MetafieldsSet($metafields: [MetafieldsSetInput!]!) {
metafieldsSet(metafields: $metafields) {
metafields {
key
namespace
value
createdAt
updatedAt
}
userErrors {
field
message
code
}
}
}
{% endcapture %}
{% assign metafield = hash %}
{% assign metafield["ownerId"] = metafield_owner_id %}
{% assign metafield["namespace"] = "demo" %}
{% assign metafield["key"] = "demo" %}
{% assign metafield["type"] = "json" %}
{% assign metafield["value"] = metafield_value | json %}
{% assign metafields = array %}
{% assign metafields = metafields | push: metafield %}
{% assign variables = hash %}
{% assign variables["metafields"] = metafields %}
{% action "shopify" query: query, variables: variables %}{
"pdf": {
"html": HTML,
...
}
}{% capture html %}
<link rel="preconnect" href="https://fonts.googleapis.com">
<link rel="preconnect" href="https://fonts.gstatic.com" crossorigin>
<link href="https://fonts.googleapis.com/css2?family=Liu+Jian+Mao+Cao&display=swap" rel="stylesheet">
<style>p { font-family: 'Liu Jian Mao Cao', cursive; }</style>
<p>Almost before we knew it, we had left the ground.</p>
<div id="tester" style="width:100%;height:40vh;"></div>
<script src="https://cdn.plot.ly/plotly-2.2.0.min.js"></script>
<script>
// from https://plotly.com/javascript/getting-started/
TESTER = document.getElementById('tester');
Plotly.newPlot( TESTER, [{
x: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5],
y: [1, 2, 4, 8, 16] }], {
margin: { t: 0 } } );
</script>
{% endcapture %}
{% action "files" %}
{
"file.pdf": {
"pdf": {
"html": {{ html | json }},
"page_width": "7in",
"page_height": "5in",
"margin_top": "10mm",
"margin_right": "10mm",
"margin_bottom": "10mm",
"margin_left": "10mm"
}
}
}
{% endaction %}{% capture query %}
query {
product(id: {{ product_id | json }}) {
id
# additional fields as needed
}
}
{% endcapture %}
{% assign result = query | shopify %}
{% assign product = result.data.product %}{% assign product = shop.products[product_id] %}
{% log
title: product.title,
status: product.status,
type: product.product_type,
description: product.body_html,
tags: product.tags,
image: product.image.src
%}{% capture query %}
query {
product(id: {{ product_id | json }}) {
id
title
status
productType
descriptionHtml
tags
featuredImage {
url
}
}
}
{% endcapture %}
{% log
title: product.title,
status: product.status,
type: product.productType,
description: product.descriptionHtml,
tags: product.tags,
image: product.featuredImage.url
%}Performing HTTP requests
Sending requests to the Shopify Admin API
Upload files to Google Drive
Google Sheets
Create, Update, Export Google Sheets
Report Toaster
Requesting reports from Report Toaster, or updating data within Report Toaster
Slack
Posting messages to Slack








Each action run is performed. During this phase, Mechanic executes each action, given the options that were provided for it by the task run's result.
Unscheduled
The run has not been assigned a time to be performed
Scheduled
Scheduled to be performed, but that time has not yet arrived
Due
The run is ready to be performed, and is waiting for a runner
Started
The run is being performed
Failed
The run has been performed, and an error has been recorded
Succeeded
The run has been performed, without errors

account
string
Required: the Google account email address to authenticate with
uploads
hash
Required: a has specifying files to upload and their contents
overwrite
boolean
Optional: when true, files with matching names will be overwritten. Defaults to false
[path/filename]
string | hash
One or more file paths mapped to their content. Paths can include folders (e.g., 'reports/monthly/file.txt'). Content can be either a direct string or a file generator object.
body
hash
Required: for creating/editing sheets and files, the object that contains a JSON representation of the properties and content of the file; for listing files, this optional object will contain the query parameters used for filtering, pagination, etc.
account
string
Required: the Google account email address to authenticate with. Must match one of the Google accounts linked in the Mechanic authentication settings.
method
string
Required: the HTTP verb as required by the Google API for the specific method (e.g. "GET", "POST", "PATCH")
url_path
string
Required: the API endpoint for the relevant Google Drive service (e.g. "/drive/v3/files")
headers
hash
Required: different combinations of API endpoints and usage will dictate which headers are required. Review the Google API docs for more details.
Mechanic will use the following headers if they are missing and the request meets certain conditions.
expires_at
An ISO8601 timestamp, specifying when the file will expire
mime_type
The MIME type of the generated file
name
The filename, as given in the original action options
size
The size of the generated file, in bytes
url
The URL at which this file will be available, until it expires
Downloads and returns a file
Accepts its own set of file generators, returning a ZIP archive of the results
Uses file generators to prepare email attachments
Uses file generators to prepare temporary URLs, from which the generated files can be downloaded
Uses file generators to prepare FTP uploads
Adds generated files to a multipart/form-data HTTP request
To inspect and respond to the results of an HTTP action, add a task subscription to mechanic/actions/perform, allowing the action to re-invoke the task with the action result data.
Learn more: Responding to action results
The action type is always a string, having a value that corresponds to a supported action (e.g. "shopify", or "http").
Action options vary by action type. Depending on the action type, its options may be another complete object, or an array, or a scalar value.
Mechanic reserves a small set of double-underscore parameters for controlling how an action is handled. These control parameters include:
__perform_event, which you can set to false to skip emitting the follow-up mechanic/actions/perform event for that specific action (the default is to emit it).
__meta, which moves the provided value into the action's meta field so you can attach meta data while using any action tag syntax.
Examples:
Actions may optionally include meta information, annotating the action with any JSON value.
When you're using the action tag, you can attach meta in a few ways:
Provide a meta object alongside options when you're supplying an options hash.
Supply meta as the second positional argument when the options are a hash.
Use the __meta control parameter with any action tag syntax to move the value into the action's meta.
This information could be purely for record-keeping, making it easy to determine why an action was rendered, or to add helpful context:
Or, this information could be used to facilitate complex task flows, in concert with a subscription to mechanic/actions/perform (see Responding to action results). An action's meta information can supply followup task runs with information about state, allowing the task to cycle between different phases of operation.
{% if customer.email contains "gmail.com" %}
{% log message: "got a gmail user!", email: customer.email %}
{% else %}
{% log message: "got someone else!", email: customer.email %}
{% endif %}reports/monthly/report.pdf # Three levels deep
data/2024/q1/sales.csv # Four levels deep
archives/backups/files.zip # Three levels deep{% action "google_drive" %}
{
"account": "[email protected]",
"uploads": {
"simple.txt": "Hello world!"
}
}
{% endaction %}{% action "google_drive" %}
{
"account": "[email protected]",
"uploads": {
"overwrite": true,
"report.pdf": {
"pdf": {
"html": "<h1>Monthly Report</h1><p>This is a PDF generated from HTML</p>"
}
},
"data.csv": "Date,Value\n2024-01-01,100"
}
}
{% endaction %}{% action "google_drive" %}
{
"account": "[email protected]",
"uploads": {
"overwrite": true,
"reports/monthly/sales.pdf": {
"pdf": {
"html": "<h1>Monthly Sales Report</h1><p>Data for this month</p>"
}
},
"data/exports/stats.csv": "Date,Value\n2024-01-01,100",
"archive/backups/data.zip": {
"zip": {
"files": {
"readme.txt": "Backup files",
"data.csv": "id,value\n1,test"
}
}
}
}
}
{% endaction %}{% capture report_content %}
<h1>{{ shop.name }} - Monthly Report</h1>
<p>Generated on {{ "now" | date: "%Y-%m-%d" }}</p>
<ul>
{% for order in shop.orders %}
<li>{{ order.name }}</li>
{% endfor %}
</ul>
{% endcapture %}
{% action "google_drive" %}
{
"account": {{ options.google_account | json }},
"uploads": {
"overwrite": true,
"inventory-report.pdf": {
"pdf": {
"html": {{ report_content | strip | json }}
}
}
}
}
{% endaction %}{
"uploads": {
[filepath: string]: {
"id": string, // Google Drive file ID
"name": string, // File name as stored in Drive
"mime_type": string, // MIME type of the uploaded file
"web_view_link": string, // URL to view the file in Google Drive
"path": string // Full folder path where file was created
}
}
}{
"uploads": {
"reports/monthly/report.pdf": {
"id": "1ABC...xyz",
"name": "report.pdf",
"mime_type": "application/pdf",
"web_view_link": "https://drive.google.com/file/d/1ABC...xyz/view",
"path": "reports/monthly"
}
}
}"Accept": "application/json",
"Content-Type": "application/json"{% action "google" %}
{
"account": "[email protected]",
"method": "POST",
"url_path": "/upload/drive/v3/files?uploadType=media",
"headers": {
"Accept": "application/json",
"Content-Type": "text/plain"
},
"body": "Hello world!"
}
{% endaction %}{% action "google" %}
{
"account": "[email protected]",
"method": "PATCH",
"url_path": "/upload/drive/v3/files/{{ google_file_id }}?uploadType=media",
"headers": {
"Accept": "application/json",
"Content-Type": "text/plain"
},
"body": "Hello again world!"
}
{% endaction %}{% action "google" %}
{
"account": "[email protected]",
"method": "GET",
"url_path": "/drive/v3/files",
"headers": {
"Accept": "application/json",
"Content-Type": "application/json"
},
"body": {
"q": "name contains 'Mechanic'",
"pageSize": 10,
"fields": "files(id,name,mimeType,createdTime)",
"trashed": false
}
}
{% endaction %}{% action "google" %}
{
"account": "[email protected]",
"method": "POST",
"url_path": "/sheets/v4/spreadsheets",
"headers": {
"Accept": "application/json",
"Content-Type": "application/json"
},
"body": {
"properties": {
"title": "Sheet File Title"
},
"sheets": [
{
"properties": {
"title": "Sheet Tab Name"
},
"data": [
{
"rowData": [
{
"values": [
{
"userEnteredValue": {
"stringValue": "Order name"
}
},
{
"userEnteredValue": {
"stringValue": "Date"
}
}
]
{
"values": [
{
"userEnteredValue": {
"stringValue": "#1357"
}
},
{
"userEnteredValue": {
"stringValue": "2025-10-05T12:00:00Z"
}
}
]
}
]
}
]
}
]
}
}
{% endaction %}{
"type": "google",
"run": {
"ok": true,
"result": {
"status": 200,
"body": {
...
}
}
}
}mechanic/user/trigger
mechanic/actions/perform{% if event.topic == "mechanic/user/trigger" %}
{% action "files" %}
{
"journal.txt": "hello world!",
"table.csv": "Title,SKU\nRed T-Shirt,TEE-R",
"invoice.pdf": {
"pdf": {
"html": "<h1>Order #12345</h1>\n<p>It's due!</p>"
}
},
"secure.zip": {
"zip": {
"password": "opensesame",
"files": {
"confirmations.txt": "this data is protected with zipcrypto encryption"
}
}
},
"external.jpg": {
"url": "https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/en/a/a9/Example.jpg"
}
}
{% endaction %}
{% elsif event.topic == "mechanic/actions/perform" and action.type == "files" %}
{% capture email_body %}
<p>The following file(s) have been generated:</p>
<ul>
{% for keyval in action.run.result %}
{% assign filename = keyval[0] %}
{% assign file = keyval[1] %}
<li><a href="{{ file.url }}">{{ filename }}</a> ({{ file.size }} bytes)</li>
{% endfor %}
</ul>
<p>-Mechanic</p>
{% endcapture %}
{% action "email" %}
{
"to": "[email protected]",
"subject": {{ action.run.result | size | append: " file(s) generated" | json }},
"body": {{ email_body | json }}
}
{% endaction %}
{% endif %}{% if event.preview %}
{% capture product_json %}
{
"admin_graphql_api_id": "gid://shopify/Product/1234567890",
"product_type": "Widget",
"status": "active",
"tags": "my-tag, some-other-tag"
}
{% endcapture %}
{% assign product = product_json | parse_json %}
{% endif %}
{% assign product_tags = product.tags | split: ", " %}
{% if product.status == "active" and product.product_type == "Widget" %}
{% if product.tags contains "my-tag" %}
{% log
message: "This product qualifies",
product: product
%}
{% endif %}
{% endif %}{% capture query %}
query {
product(id: {{ product.admin_graphql_api_id | json }}) {
status
productType
tags
}
}
{% endcapture %}
{% if event.preview %}
{% capture result_json %}
{
"data": {
"product": {
"id": "gid://shopify/Product/1234567890",
"productType": "Widget",
"status": "ACTIVE",
"tags": [
"my-tag",
"some-other-tag"
]
}
}
}
{% endcapture %}
{% assign result = result_json | parse_json %}
{% endif %}
{% assign product = result.data.product %}
{% if product.status == "ACTIVE" and product.productType == "Widget" %}
{% if product.tags contains "my-tag" %}
{% log
message: "This product qualifies",
product: product
%}
{% endif %}
{% endif %}{% capture query %}
query {
shop {
name
}
}
{% endcapture %}
{% assign result = query | shopify %}
{% log result.data.shop.name %}{% assign cursor = nil %}
{% assign total_inventory = 0 %}
{% for n in (0..100) %}
{% capture query %}
query {
products(
first: 250
after: {{ cursor | json }}
) {
pageInfo {
hasNextPage
}
edges {
cursor
node {
totalInventory
}
}
}
}
{% endcapture %}
{% assign result = query | shopify %}
{% if event.preview %}
{% capture result_json %}
{
"data": {
"products": {
"edges": [
{
"node": {
"totalInventory": -4
}
}
]
}
}
}
{% endcapture %}
{% assign result = result_json | parse_json %}
{% endif %}
{% for product_edge in result.data.products.edges %}
{% assign product = product_edge.node %}
{% assign total_inventory = total_inventory | plus: product.totalInventory %}
{% endfor %}
{% if result.data.products.pageInfo.hasNextPage %}
{% assign cursor = result.data.products.edges.last.cursor %}
{% else %}
{% break %}
{% endif %}
{% endfor %}{
FILE_GENERATOR_TYPE: FILE_GENERATOR_OPTIONS
}{% action "files" %}
{
"invoice.pdf": {
"pdf": {
"html": "<h1>Order #12345</h1>\n<p>It's due!</p>"
}
},
"external.jpg": {
"url": "https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/en/a/a9/Example.jpg"
},
"plain.txt": "This\nis\na\nmulti-line\nplaintext\nfile."
}
{% endaction %}{% assign customers = bulkOperation.objects | where: "__typename", "Customer" %}mechanic/user/trigger
mechanic/shopify/bulk_operation{% if event.topic == "mechanic/user/trigger" %}
{% capture bulk_operation_query %}
query {
customers {
edges {
node {
__typename
id
email
}
}
}
}
{% endcapture %}
{% action "shopify" %}
mutation {
bulkOperationRunQuery(
query: {{ bulk_operation_query | json }}
) {
bulkOperation {
id
status
}
userErrors {
field
message
}
}
}
{% endaction %}
{% elsif event.topic == "mechanic/shopify/bulk_operation" %}
{% assign customers = bulkOperation.objects | where: "__typename", "Customer" %}
{% assign emails = customers | map: "email" %}
{% log emails: emails %}
{% endif %}{
"action": {
"type": ACTION_TYPE,
"options": ACTION_OPTIONS,
"meta": ACTION_META
}
}{%- action "http", method: "get", url: "https://postman-echo.com/get", __perform_event: false -%}{%- assign meta = hash -%}
{%- assign meta["source"] = "cache" -%}
{%- action "cache", "set", "foo", "bar", __meta: meta -%}{%- assign options = hash -%}
{%- assign options["method"] = "post" -%}
{%- assign options["url"] = "https://postman-echo.com/post" -%}
{%- assign meta = hash -%}
{%- assign meta["mode"] = "initial_request" -%}
{%- action "http", options: options, meta: meta -%}{%- assign options = hash -%}
{%- assign options["method"] = "post" -%}
{%- assign options["url"] = "https://postman-echo.com/post" -%}
{%- assign meta = hash -%}
{%- assign meta["mode"] = "initial_request" -%}
{%- action "http", options, meta -%}{%- assign meta = hash -%}
{%- assign meta["note"] = "graphql" -%}
{%- action "shopify", __meta: meta -%}
mutation {
tagsAdd(id: "gid://shopify/Customer/1234567890", tags: ["vip"]) {
node { id }
userErrors { field message }
}
}
{%- endaction -%}{
"action": {
"type": "shopify",
"options": [
"post",
"/admin/customers/1234567890/send_invite.json",
{}
],
"meta": {
"invite_reason": "alpha",
"customer_email": "[email protected]"
}
}
}{% if event.topic contains "trigger" %}
{% action %}
{
"type": "cache",
"options": ["set", "foo", "bar"],
"meta": {
"mode": "first"
}
}
{% endaction %}
{% elsif action.meta.mode == "first" %}
{% action %}
{
"type": "cache",
"options": ["set", "foo", "bar"],
"meta": {
"mode": "second"
}
}
{% endaction %}
{% elsif action.meta.mode == "second" %}
{% action "echo", "done" %}
{% endif %}
A task uses its preview to demonstrate what actions the task intends to generate. Among other purposes (see below), this is also how tasks request the Shopify permissions they require.
Mechanic generates a task preview by rendering the task code using a preview event, which resembles a live event that the task may see. The task is then responsible for rendering preview actions in response to the preview event, actions which are visually presented to the user and are analyzed by the platform, but are never actually performed.
A preview has three critical purposes:
Showing the user that the task will do what they expect it to do
Showing the task developer that the task code is functioning as intended
Showing the Mechanic platform what permissions the task requires
Core to the design of Mechanic is the idea that we can make it easy to make it easy – in this case, making it easy for developers to show their users what a Mechanic task can be expected to do.
By rendering preview actions, a task can prove to the user that it is interpreting their configuration as they intended. For example, by rendering a preview action, a task can show the user that their configured email content is appearing as expected inside the email body. This increases trust in the task, and allows users confidence in the task's outcome, even before the task processes a live event.
Developers may think of previews as a sort of test, using preview actions to prove that their task code is functioning as intended. A quality task will exercise all of its code in response to a preview event; doing so gives the developer instant feedback on task results, without actually having to run the task with a live event.
At the platform level, Mechanic uses previews to determine what permissions a task requires.
Mechanic gets this information from the actions that a task generates during preview, as well as from analysis of the Liquid lookups and GraphQL queries that a task uses during runtime.
For example, if a task renders a action containing a mutation, Mechanic will prompt the user to grant access to the write_customers Shopify OAuth scope. If Mechanic observes a task using shop.customers, or observes the filter receiving a customer-related GraphQL query, it will prompt for the read_customers scope.
Some GraphQL mutations have multiple potential scope requirements, like or . Because the requirements of these mutations hinge on their arguments, make sure that your preview actions are rendered with realistic ID strings (e.g. id: "gid://shopify/Product/12345"). Mechanic will look for these IDs to determine what scopes to request.
Previews are generated using synthetic, temporary, non-persisted events – at least one for each event topic that the task subscribes to. These events are sourced from one of three places, in order of priority:
If the task for a given topic, the preview will use the defined event;
Or, if the Mechanic account has a recent event with a matching topic on file, the preview will use data from that event;
Or, if the event topic is standard and known to Mechanic (i.e. not a part of ), the preview will use illustrative example event data defined by the Mechanic platform.
A preview event is identical to a live event in all respects but one: it contains a preview attribute, set to true, identifying it as a preview event.
For live events, the preview attribute does not exist. This means that event.preview == false is not a valid way to detect a live event. Instead, use event.preview != true, or event.preview == nil.
A preview event's data is taken from the Mechanic account's event history, providing a realistic sample of the data a task can expect to see. (If the account history has no events for a given topic just yet, Mechanic will attempt to use anonymous sample event data of its own.)
A developer can choose between rendering static and dynamic preview actions. Static preview actions are hard-coded, written to appear whenever event.preview is true. Dynamic preview actions are the result of the task code running normally, using event data in preview in the same way that it would use that event data with a live event. Because dynamic preview actions are the result of meaningfully exercising the task's code, they can provide a good indicator of how the task will behave with a live event. By contrast, static preview actions do not provide useful feedback on how a task is coded.
A static preview action is rendered in direct response to event.preview. In general, it's better to use , but an understanding of both techniques is useful.
In the following example, a static preview action demonstrates that the task intends to tag incoming orders with "web". In actuality, the task's intent is to only tag orders that arrive via the Online Store channel; because the task can't be sure whether or not the preview event will contain such an order, a static preview action is used to ensure that a preview event always results in a tagging action.
Branching a task like this has two problems:
The actual condition of the task is not exercised during preview. The task will need to be tested with live orders from multiple channels, in order to verify that the task works properly.
Duplicating code makes it easier for one copy of the code to fall out of date. By using completely different code for the preview and live actions, it becomes easier for developers to forget to keep the two copies in sync as the task evolves.
Subscriptions
A dynamic preview action is the natural result of exercising a task's code as completely as possible, without adding any business logic that responds to event.preview. Put another way, the idea is to make the preview (that appears during task editing) look as similar to a live event as possible.
There are two techniques available for "steering" the task towards desired outcomes during preview.
Use to control preview event data, without ever having to add preview-related code to the task itself. This is the cleanest way to control data provided by the event during preview.
Use to dynamically swap in preview-friendly values. This is generally not necessary for preview event data, but may be necessary when querying Shopify for data during a task: because the Shopify API is disabled during preview, using stub data can be useful for swapping in realistic values that would be returned during a live run.
Stub data is hard-coded into a task, providing an unchanging source of data for previews. It is an important tool when generating dynamic preview actions. Stub data may be used for user-defined variables, but may also override environment variables as needed.
Most tasks make decisions based on the automatically provided, making it a common practice to stub them during preview mode. Any and all Liquid variables may be replaced by stub data, including event and any .
In simple cases, replacement objects may be constructed using the tag.
It's also possible to construct this data using .
Mechanic makes GraphQL data available to tasks via the filter. Mechanic observes the shopify filter in action during preview mode, using its inputs to inform Mechanic's knowledge of what permissions the task needs.
For this reason, it's important to allow the shopify filter to run normally, and construct stub data afterwards.
It can be useful to specify stub data using JSON, fed through the filter. Sample JSON is easy to generate using .
The Event action is for generating custom events in the User event domain. It's used to queue up follow-up work, either immediately or in the future, and can be useful when designing complex workloads, separating work between tasks.
Events generated by this action may be responded to by other tasks, or by the task that generated this action.
Events generated by this action are child events of the event responsible for the current action.
If a run_at value specifies a time in the past, the new event will be run immediately.
Tasks specified by task_ids or task_id must subscribe to the event topic being used. As with all subscriptions, may be used, and will be respected.
Uses the optional task_id parameter to control which singular task is allowed to respond to this event.
That task must be subscribed to the event topic being used.
You can limit a task to itself by referencing it's own task.id
See to have a user configurable input instead of hardcoding the task id(s).
This example uses the run_at option to run the task at a later scheduled time.
This task emails a customer daily until their order is paid. It works by scheduling a follow-up run of the same task, one day in the future, using the run_at option.
Subscriptions
Code
This task emails a customer daily until their order is paid. It works by firing the follow-up event immediately, using a subscription offset to respond to it a day later.
Subscriptions
Code

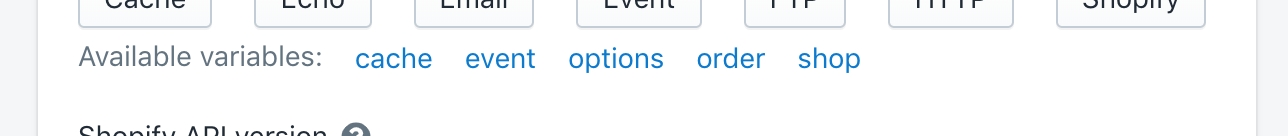
topic
Required; a string specifying an event topic of the form "user/*/*"
data
Required; any JSON value (including null), to be used as the event data
run_at
Optional; a Unix timestamp integer, or any string that can be parsed as a time
task_ids
Optional, cannot be used with task_id; an array of task UUID strings, specifying which tasks are allowed to respond to this event
task_id
Optional, cannot be used with task_ids; a string containing a single task UUID, specifying which task is allowed to respond to this event
{% assign data = hash %}
{% assign data["foo"] = "bar" %}
{% action "event", topic: "user/foo/bar", data: data %}{% if event.preview %}
{% log "This is a preview event, generated by Mechanic." %}
{% else %}
{% log "This is a live event, received by Shopify." %}
{% endif %}
{% if event.preview != true %}
{% log "This is a live event, received by Shopify." %}
{% else %}
{% log "This is a preview event, generated by Mechanic." %}
{% endif %}{% if event.preview %}
{% action "shopify" %}
mutation {
tagsAdd(id: "gid://shopify/Order/1234567890", tags: "web") {
userErrors { field, message }
}
}
{% endaction %}
{% elsif order.source_name == "web" %}
{% action "shopify" %}
mutation {
tagsAdd(id: {{ order.admin_graphql_api_id | json }}, tags: "web") {
userErrors { field, message }
}
}
{% endaction %}
{% endif %}shopify/orders/create{% if some_evaluated_condition %}
{% action "shopify" %}
mutation {
tagsAdd(id: {{ order.admin_graphql_api_id | json }}, tags: "web") {
userErrors { field, message }
}
}
{% endaction %}
{% endif %}{% if event.preview %}
{% assign order = hash %}
{% assign order["source_name"] = "web" %}
{% assign order["admin_graphql_api_id"] = "gid://shopify/Order/1234567890" %}
{% endif %}
{% if order.source_name == "web" %}
{% action "shopify" %}
mutation {
tagsAdd(id: {{ order.admin_graphql_api_id | json }}, tags: "web") {
userErrors { field, message }
}
}
{% endaction %}
{% endif %}{% if event.preview %}
{% capture order_json %}
{
"source_name": "web",
"admin_graphql_api_id": "gid://shopify/Order/1234567890"
}
{% endcapture %}
{% assign order = order_json | parse_json %}
{% endif %}
{% if order.source_name == "web" %}
{% action "shopify" %}
mutation {
tagsAdd(id: {{ order.admin_graphql_api_id | json }}, tags: "web") {
userErrors { field, message }
}
}
{% endaction %}
{% endif %}{% capture query %}
query {
publications(first: 250) {
edges {
node {
id
name
}
}
}
}
{% endcapture %}
{% assign result = query | shopify %}
{% if event.preview %}
{% capture result_json %}
{
"data": {
"publications": {
"edges": [
{
"node": {
"id": "gid://shopify/Publication/69217648807",
"name": "Online Store"
}
}
]
}
}
}
{% endcapture %}
{% assign result = result_json | parse_json %}
{% endif %}
{% log available_publications: result.data.publications %}{% assign cursor = nil %}
{% assign total_inventory = 0 %}
{% for n in (0..100) %}
{% capture query %}
query {
orders(
first: 250
query: "status:open"
after: {{ cursor | json }}
) {
pageInfo { hasNextPage }
edges {
node { name, email }
}
}
}
{% endcapture %}
{% assign result = query | shopify %}
{% if event.preview %}
{% capture result_json %}
{
"data": {
"orders": {
"pageInfo": {
"hasNextPage": false
},
"edges": [
{
"node": {
"name": "#1135",
"email": "[email protected]"
}
}
]
}
}
}
{% endcapture %}
{% assign result = result_json | parse_json %}
{% endif %}
{% for order_edge in result.data.orders.edges %}
{% assign order_node = order_edge.node %}
{% if order_node.email == blank %}
{% continue %}
{% endif %}
{% action "email" %}
{
"to": {{ order_node.email | json }},
"subject": {{ "We're still working on " | append: order_node.name | json }},
"body": "Thanks for your patience!"
}
{% endaction %}
{% endfor %}
{% if result.data.orders.pageInfo.hasNextPage %}
{% assign cursor = result.data.orders.edges.last.cursor %}
{% else %}
{% break %}
{% endif %}
{% endfor %}{% assign data = hash %}
{% assign data["foo"] = "bar" %}
{% assign task_id = "293b7040-6689-4eb1-8b5d-64f4d33eb2ae" %}
{% comment %} For multiple tasks use `task_ids` {% endcomment %}
{% action "event", topic: "user/foo/bar", data: data, task_id: task_id %}{% assign one_day_in_seconds = 60 | times: 60 | times: 24 %}
{% action "event" %}
{
"topic": "user/foo/bar",
"task_id": {{ task.id | json }},
"run_at": {{ "now" | date: "%s" | plus: one_day_in_seconds | json }},
"data": {
"foo": "bar"
}
}
{% endaction %}shopify/orders/create
user/orders/unpaid_reminder{% if event.preview %}
{% assign order = hash %}
{% assign order["id"] = 1234568790 %}
{% assign order["name"] = "#1234" %}
{% elsif event.topic == "user/orders/unpaid_reminder" %}
{% assign order = shop.orders[event.data.order_id] %}
{% endif %}
{% unless order.financial_status == "paid" %}
{% action "email" %}
{
"to": {{ order.email | json }},
"reply_to": {{ shop.customer_email | json }},
"subject": "Order {{ order.name }} still needs to be paid",
"body": "Please get in touch, stat!",
"from_display_name": {{ shop.name | json }}
}
{% endaction %}
{% assign one_day_in_seconds = 60 | times: 60 | times: 24 %}
{% action "event" %}
{
"topic": "user/orders/unpaid_reminder",
"task_id": {{ task.id | json }},
"run_at": {{ "now" | date: "%s" | plus: one_day_in_seconds | json }},
"data": {
"order_id": {{ order.id | json }}
}
}
{% endaction %}
{% endunless %}shopify/orders/create
user/orders/unpaid_reminder+1.day{% if event.preview %}
{% assign order = hash %}
{% assign order["id"] = 1234568790 %}
{% assign order["name"] = "#1234" %}
{% elsif event.topic == "user/orders/unpaid_reminder" %}
{% assign order = shop.orders[event.data.order_id] %}
{% endif %}
{% unless order.financial_status == "paid" %}
{% action "email" %}
{
"to": {{ order.email | json }},
"reply_to": {{ shop.customer_email | json }},
"subject": "Order {{ order.name }} still needs to be paid",
"body": "Please get in touch, stat!",
"from_display_name": {{ shop.name | json }}
}
{% endaction %}
{% assign one_day_in_seconds = 60 | times: 60 | times: 24 %}
{% action "event" %}
{
"topic": "user/orders/unpaid_reminder",
"task_id": {{ task.id | json }},
"data": {
"order_id": {{ order.id | json }}
}
}
{% endaction %}
{% endunless %}The Google Sheets action allows you to interact with Google Sheets. It supports creating new spreadsheets, appending data to existing sheets, and exporting spreadsheets in various formats. Mechanic interacts with Google Sheets via the Google Sheets API, using OAuth2 for authentication.
Adds new rows to an existing spreadsheet.
account
spreadsheet_id
rows
sheet_name (defaults to "Sheet1")
Creates a new spreadsheet, optionally with initial data.
account
title
folder_path (path where spreadsheet should be created)
rows (initial data to populate the spreadsheet)
Exports a spreadsheet in various formats.
account
spreadsheet_id
file_type
xlsx (default)
csv
This action requires connecting a Google account with the appropriate permissions. To connect an account:
Go to the Settings screen
Click Authentication
Follow the Google account connection flow from the Google tab
The action can only access spreadsheets it creates, no other spreadsheets in your drive.
When creating spreadsheets, you can specify a folder path to organize your files:
Use forward slashes to separate folder names (e.g., "reports/2024/monthly")
Folders will be created if they don't exist
Can only access folders created by this integration
Invalid characters not allowed: < > : " / \ | ? *
The action returns different responses based on the operation performed:
Example:
Example:
Connect your AI assistant to Mechanic's task library and documentation. The Mechanic Model Context Protocol (MCP) server enables your AI assistant to search tasks, explore documentation, and fetch task code.
Your AI assistant uses the MCP server to read and interact with Mechanic's resources:
Ask your AI assistant to help with Mechanic task development or automation questions.
The assistant searches Mechanic's task library and documentation based on your prompt.
The MCP server provides access to 350+ pre-built tasks and comprehensive Mechanic documentation, so your assistant can provide accurate code, solutions, and guidance based on current best practices.
Before you set up the Mechanic MCP server, make sure you have:
Node.js 18 or higher installed on your system.
An AI development tool that supports MCP, such as Claude Desktop, Claude Code, Cursor, Codex CLI, or Gemini CLI.
After you set up the MCP server, you can ask your AI assistant questions like:
"Find tasks that auto-tag orders"
"How do I subscribe to Shopify product creation events?"
"Show me the code for the 'Auto-tag customers by order tier' task"
"What tasks use the bulk operations API?"
Your AI assistant will use the MCP server to search Mechanic's task library and documentation when providing responses.
The MCP server provides access to:
350+ pre-built automation tasks from
Complete Mechanic documentation from
Task subscriptions, options, and full Liquid scripts
Documentation on Liquid templating, actions, events, and integrations
The server runs locally in your development environment and doesn't require authentication.
Add configuration code that tells your AI tool how to connect to and use the Mechanic MCP server. This configuration enables your AI assistant to automatically access Mechanic's task library and documentation when you ask questions.
For Claude Desktop:
Open the app and access your configuration file through settings
Add the JSON configuration below to your MCP servers section
Save and restart Claude Desktop
For Claude Code:
Run this command in your terminal:
Restart Claude Code to load the server
Manual JSON configuration (both):
Open Cursor and go to Cursor > Settings > Cursor Settings > Tools and integrations > New MCP server.
Add this configuration to your MCP servers:
Save your configuration and restart Cursor.
Add this configuration to your ~/.codex/config.toml file:
Restart Codex to load the new MCP server configuration.
Add this configuration using the Gemini CLI:
Restart Gemini CLI to load the new MCP server configuration.
The Mechanic MCP server provides the following tools:
search_tasksSearch across Mechanic's task library to find tasks matching your query. Returns task titles, descriptions, tags, subscriptions, and public URLs.
Best for discovering existing automation solutions before building custom tasks. Results include subscription event topics, task options, and tags for filtering.
Parameters:
query (required): Search terms to match against task titles, descriptions, and content
limit (optional): Maximum number of results to return (default: 10, max: 50)
offset (optional): Number of results to skip for pagination (default: 0)
search_docsSearch across all Mechanic documentation to find relevant pages matching your query. Returns documentation titles, paths, and public URLs.
Best for learning about Mechanic concepts, Liquid templating, actions, and platform features. Returns quick results from across the entire documentation site.
Parameters:
query (required): Search terms to match against documentation content
limit (optional): Maximum number of results to return (default: 10, max: 50)
offset (optional): Number of results to skip for pagination (default: 0)
get_taskRetrieve complete task details including subscriptions, Liquid script, options, and JavaScript blocks. Use this to see the full implementation of a specific task.
Parameters:
id (required): Task handle or ID (e.g., "auto-tag-customers-by-sales-channel" or "task:auto-tag-customers-by-sales-channel")
Returns:
Task metadata (name, tags, URL)
Event subscriptions and subscription template
Complete Liquid script
Task options with defaults
get_docRetrieve the full content of a documentation page. Provides complete documentation context without chunking.
Parameters:
id (required): Documentation ID from search results (e.g., "doc:core/tasks/code/action-objects.md")
Returns:
Full markdown content
Documentation title and path
Public documentation URL
similar_tasksFind tasks related to a specific task by analyzing shared tags, event subscriptions, and title similarity. Useful for discovering alternative approaches or complementary automations.
Parameters:
handle (required): Task handle or ID to find similar tasks for
limit (optional): Maximum number of similar tasks to return (default: 10)
refresh_indexRefresh and rebuild the search index from bundled data. Generally not needed as the server includes pre-built indexes.
When working with your AI assistant and the Mechanic MCP server:
Discover before building: Search for existing tasks before creating custom solutions. The library contains 350+ battle-tested tasks.
Use GraphQL: Prefer Shopify's GraphQL Admin API in task code. REST is deprecated in Mechanic.
Reference public URLs: Always cite tasks using their public URLs (tasks.mechanic.dev) and docs using learn.mechanic.dev URLs.
Get full task details
- Browse and contribute to Mechanic's task library
- Learn how to write Mechanic tasks
- Mechanic's Liquid implementation
- Available action types for tasks
The Email action is for sending email. ✅ It supports the store's email templates, and supports attachments constructed by file generators.
Mechanic sends email via Postmark, our email provider. Currently, Mechanic only supports Postmark's transactional message stream, which means that marketing and other bulk mail may not be sent. To learn more about what is and isn't a transactional message, see Postmark's article: "What are Transactional emails?".
Mechanic parses each email body for HTML and CSS, allowing authors to use <style> tags without having to think about email client compatibility.
Images may be embedded using the <img> tag, but must be hosted independently. Shopify provides basic file hosting, appropriate for uploading images for use with Mechanic emails. To learn more, see .
This action only supports sending from a single address (regardless of the sender name, as controlled by the from_display_name option).
By default, the sender address is a Mechanic address based on the store's myshopify.com subdomain. For example, the store example.myshopify.com will default to having its mail sent from [email protected].
Changing the sender address involves adding it to the store's Mechanic account, and then configuring the email domain name with some DNS records for verification.
For more on this, see .
To achieve easily reusable headers and footers, Mechanic can be configured with one or more email templates, available in the Mechanic account settings. To learn more about configuring email templates, see .
To use a specific email template with the Email action, use the template option to specify the name of the desired email template.
All options used with the Email action will be made available as Liquid variables for the email template. This means that standard options may be used, like {{ subject }} and {{ body }}, and also custom options: passing in an "order_data" option, containing order data, may allow the email template to show the order name via {{ order_data.name }}.
Note that custom options, like all task options, must be provided using standard JSON. This means that the data made available to email templates will be derived from plain JSON values.
For example, consider this action:
The template named "order_acknowledgement" could include the following Liquid, and get the expected results:
But, because order_data
This action supports attachments given in Mechanic's file generator format. This structure allows the sender to construct a variety of files, including ad-hoc text-based files, PDFs rendered from HTML, files dynamically downloaded from external locations, and ZIP files containing any other files.
For more on this, see .
Individual tasks may be optionally configured with their own documentation, formatted with Markdown, providing the user with anything they should know about the task's usage and operation.
Task documentation is shown to the user below the task's options. Documentation is also shown in the confirmation prompt a user sees when they trigger a task that subscribes to either mechanic/user/trigger or mechanic/user/text.
Task documentation may be managed in Advanced mode.
In Basic mode, documentation is displayed below the task options.
Task documentation may be formatted with Markdown, a common syntax for text formatting.
The following table comes from , and is presented with no changes, under the license.
The Markdown editor in Mechanic includes keyboard shortcuts for common formatting operations. These shortcuts can also be accessed through the right click menu in the editor.
When pasting a valid URL, if you have text selected the selected text will automatically be wrapped in Markdown link syntax using the pasted URL. The selected text becomes the link text, and the pasted URL becomes the link destination.
rows
array
Required: for append_rows and optional for create_spreadsheet; array of arrays containing the data to write
sheet_name
string
Optional: for append_rows; defaults to "Sheet1"
file_type
string
Optional: for export_spreadsheet; the format to export. One of: "xlsx" (default), "csv", "pdf", "html", "ods", "tsv"
folder_path
string
Optional: for create_spreadsheet; the folder path where the spreadsheet should be created (e.g., "reports/2024/monthly")
html
ods
tsv
account
string
Required: the Google account email address to authenticate with
operation
string
Required: the operation to perform. One of: "append_rows", "create_spreadsheet", "export_spreadsheet"
spreadsheet_id
string
Required: for append_rows and export_spreadsheet; the ID of the target spreadsheet
title
string
Required: for create_spreadsheet; the title for the new spreadsheet
"How do I use the cache action in Mechanic?"
"Find similar tasks to 'email customer when order is fulfilled'"
"Write a task that sends an email when inventory gets low"
tags (optional): Filter by task tags
subscriptions (optional): Filter by event subscription topics
fuzzy (optional): Enable fuzzy matching for typo tolerance
fuzzyMaxEdits (optional): Maximum edit distance for fuzzy matching (max: 2)
fuzzy (optional): Enable fuzzy matching for typo toleranceOrder status JavaScript (if present)
get_taskFind related work: Use similar_tasks to discover alternative approaches or complementary automations.
Events and subscriptions - Understanding Mechanic's event system
reports/monthly # Two levels deep
data/2024/q1/sales # Four levels deep
archives/exports/sheets # Three levels deep{% action "google_sheets" %}
{
"account": "[email protected]",
"operation": "append_rows",
"spreadsheet_id": "1234567890abcdef",
"sheet_name": "Orders",
"rows": [
["Order ID", "Customer", "Total"],
["1001", "John Doe", "99.99"],
["1002", "Jane Smith", "149.99"]
]
}
{% endaction %}{% action "google_sheets" %}
{
"account": "[email protected]",
"operation": "create_spreadsheet",
"title": "Monthly Sales Report",
"rows": [
["Month", "Revenue", "Expenses", "Profit"],
["January", "5000", "3000", "2000"],
["February", "5500", "3200", "2300"]
]
}
{% endaction %}{% action "google_sheets" %}
{
"account": "[email protected]",
"operation": "export_spreadsheet",
"spreadsheet_id": "1234567890abcdef",
"file_type": "pdf"
}
{% endaction %}{% assign order_rows = array %}
{% assign header_row = array %}
{% assign header_row["Order", "Customer", "Total"] %}
{% assign order_rows[header_row] %}
{% for order in shop.orders %}
{% assign order_row = array %}
{% assign order_row[order.name, order.customer.name, order.total_price] %}
{% assign order_rows[order_row] %}
{% endfor %}
{% action "google_sheets" %}
{
"account": {{ options.google_account | json }},
"operation": "append_rows",
"spreadsheet_id": {{ options.spreadsheet_id | json }},
"rows": {{ order_rows | json }}
}
{% endaction %}{% action "google_sheets" %}
{
"account": "[email protected]",
"operation": "create_spreadsheet",
"folder_path": "reports/2024/monthly",
"title": "March Sales",
"rows": [
["Date", "Revenue", "Units"],
["2024-03-01", "5000", "50"],
["2024-03-02", "6000", "60"]
]
}
{% endaction %}mechanic/user/trigger
mechanic/actions/perform
{% assign sheet_data = action.run.result.data_base64 |
base64_decode | parse_csv: headers: true %}
{% action "echo" sheet_data %}
{
"spreadsheet_id": string,
"updated_range": string,
"updated_rows": number,
"updated_columns": number,
"spreadsheet_url": string
}{
"spreadsheet_id": "1234567890abcdef",
"updated_range": "Sheet1!A1:C3",
"updated_rows": 3,
"updated_columns": 3,
"spreadsheet_url": "https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1234567890abcdef"
}{
"spreadsheet_id": string,
"spreadsheet_url": string,
"title": string
}{
"spreadsheet_id": "1234567890abcdef",
"spreadsheet_url": "https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1234567890abcdef",
"title": "Monthly Sales Report"
}{
"spreadsheet_id": string,
"spreadsheet_url": string,
"title": string,
"folder_path": string
}{
"spreadsheet_id": "1234567890abcdef",
"spreadsheet_url": "https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1234567890abcdef",
"title": "March Sales",
"folder_path": "reports/2024/monthly"
}{
"spreadsheet_id": string,
"name": string,
"size": number,
"file_type": string,
"data_base64": string
}{
"spreadsheet_id": "1234567890abcdef",
"name": "Monthly Sales Report",
"size": 12345,
"file_type": "pdf",
"data_base64": "base64encodeddata..."
}claude mcp add --scope user --transport stdio mechanic-mcp -- npx -y @lightward/mechanic-mcp@latest{
"mcpServers": {
"mechanic-mcp": {
"command": "npx",
"args": ["-y", "@lightward/mechanic-mcp@latest"]
}
}
}{
"mcpServers": {
"mechanic-mcp": {
"command": "npx",
"args": ["-y", "@lightward/mechanic-mcp@latest"]
}
}
}[mcp_servers.mechanic-mcp]
command = "npx"
args = ["-y", "@lightward/mechanic-mcp@latest"]{
"mcpServers": {
"mechanic-mcp": {
"command": "npx",
"args": ["-y", "@lightward/mechanic-mcp@latest"]
}
}
}from_display_name
Optional; a string controlling the name (but not the address) of the sender
headers
Optional; a hash of email header strings and value strings
template
Optional; a string naming an email template from the current Mechanic account
attachments
Optional; an object specifying files to attach, using
...
Additional options may be provided, and will be made available to email templates as variables, named after each option
to
Required; an array or comma-delimited string of recipient addresses
subject
Required; a string specifying the message subject
body
Required; an HTML string of body content; supports HTML and CSS
cc
Optional; an array or comma-delimited string of cc addresses
bcc
Optional; an array or comma-delimited string of bcc addresses
reply_to
Optional; a single reply-to address
code
---
[title](https://www.example.com)

: ⌘+Shift+E : Ctrl+Shift+E
Adds or removes Inline Code formatting on selected text or current word.
Toggle Code Block
: ⌘+Shift+E : Ctrl+Shift+E
Adds or removes a Code Block on multiline selection or blank line.
Toggle List
: ⌘+Shift+L : Ctrl+Shift+L
Cycles through List formats.
Toggle Link
: ⌘+Shift+K : Ctrl+Shift+K
Adds or removes Link formatting.
Toggle Blockquote
: ⌘+Shift+B : Ctrl+Shift+B
Adds or removes Blockquote formatting.
Toggle Image
: ⌘+Shift+I : Ctrl+Shift+I
Adds or removes Image formatting.
Element
Markdown Syntax
# H1 ## H2 ### H3
**bold text**
_italicized text_
> blockquote
- First item - Second item - Third item
1. First item 2. Second item 3. Third item
Action
Shortcut
Description
Toggle Bold
: ⌘+B : Ctrl+B
Adds or removes Bold formatting on selected text or current word.
Toggle Italic
: ⌘+I : Ctrl+I
Adds or removes Italic formatting on selected text or current word.
Toggle Strikethrough
: ⌘+Shift+X : Ctrl+Shift+X
Adds or removes Strikethrough on selected text or current word.
Toggle Heading
: ⌘+Shift+H : Ctrl+Shift+H
Cycles through Heading formats.



Toggle Inline Code
The HTTP action performs HTTP requests. It is commonly used to invoke third-party APIs.
To use the response from an HTTP action, add a task subscription to mechanic/actions/perform.
The HTTP action has intelligently varying behavior, based on the presence and value of the Content-Type header, and the data type of the body option.
If the Content-Type header is unspecified or set to application/json, and if the body option is set to a JSON object or array, the request body will be automatically serialized to a JSON string, and the request will contain a Content-Type header set to application/json.
If the files option is given, its contents will be evaluated for , and the results will be used to construct a multipart/form-data upload request, combining generated files with any key-value pairs found in the body option.
If the files option is not given, and if the Content-Type header is set to application/x-www-form-urlencoded, and if the body option is set to a JSON object or array, the request body will be serialized to a form-encoded string.
To authenticate a request using and the "Basic" authentication type, use something like this:
The HTTP action supports HTTPS, HTTP, and SOCKS5 proxy connections via the "proxy" option, set to a URI string beginning with https://, http://, or socks5://. When configured, Mechanic will open a connection to your proxy server, and pass your request through that connection.
We recommend using an HTTPS proxy server (rather than HTTP or SOCKS5) for a secure connection between Mechanic and your proxy. is a good option for this kind of service.
An HTTP action returns an object containing the following keys:
Because HTTP allows for the same header name to be present multiple times, this action's result specifies an array for each response header – even if the header was only present once.
To retrieve a specific header in a task responding to , use something like this:
If the response contained a Content-Type header set to application/json, the body result value will be the result of parsing the response body for JSON.
For all other cases, the body result value will be an UTF8 string, regardless of the response body's original encoding. To access the response body in its original encoding, use the body_base64 result value, passing it through the Liquid filter if necessary.
By default, this action will consider any valid HTTP response to be a success, regardless of its response code.
However, because 5xx responses should often be considered a retryable error, this action supports the error_on_5xx option. When set to true, this action will interpret any 5xx responses as an action error.
As with all runs, HTTP action errors are subject to .
This task prompts the user for text input, and submits it to a public API that returns everything submitted to it. The task then re-invokes itself, using the action to display the response status, content type, and body.
Subscriptions
Code
{% action "email" %}
{
"to": "[email protected]",
"subject": "Thanks for your order!",
"template": "order_acknowledgement",
"order_data": {{ order | json }}
}
{% endaction %}This is the first item: {{ order_data.line_items.first.title }}{% action "email" %}
{
"to": "[email protected]",
"subject": "Hello world",
"body": "It's a mighty fine day!",
"reply_to": {{ shop.customer_email | json }},
"from_display_name": {{ shop.name | json }}
}
{% endaction %}{% capture email_body %}
<b>Hello!</b>
It's fantastic to see you!
{% endcapture %}
{% action "email" %}
{
"to": "[email protected]",
"subject": "Hello world",
"body": {{ email_body | unindent | strip | newline_to_br | json }}
}
{% endaction %}{% action "email" %}
{
"to": "[email protected]",
"subject": "An image test",
"body": "Please see attached. :)",
"attachments": {
"a_configured_image_from_the_web.png": {
"url": "https://www.google.com/images/branding/googlelogo/2x/googlelogo_color_272x92dp.png"
}
}
}
{% endaction %}Remember order {{ order_data.customer.orders.any.first.number }}, your first ever?**text**_text_~text~→ H1 → H2 → H3 → Plain Text
→ # text → ## text → ### text → text → [selected text](https://pastedurl.com)headers
Hash, optional
May be set to a JSON object, mapping header names to header values
follow_redirects
Boolean, optional
Defaults to true, may be set to false; controls whether or not 3xx responses with Location headers are automatically followed to their destination
proxy
String, optional
May be a proxy URI string beginning with https://, http://, or socks5://; see "Using a proxy" below
verify
Boolean, optional
May be set to false to disable SSL certificate verification
error_on_5xx
Boolean, optional
May be set to true to have 5xx HTTP response codes be considered action errors
method
String, required
Must be one of "options", "head", "get", "post", "put", "patch", or "delete"
url
String, required
Must start with https:// or http://
body
String, required for non-GET requests
Format varies, see below
files
Hash, optional
May be set to a JSON object, mapping filenames to file generators
status
An integer, specifying the response code
headers
An object containing response headers, where each key is a string and each value is an array of values found for that header
body
The interpreted value of the response body; see below
body_base64
The original response body, encoded using base64
{% action "http" %}
{
"method": "post",
"url": "https://postman-echo.com/post",
"body": {
"hello": "world"
},
"files": {
"robots.txt": {
"url": "https://www.shopify.com/robots.txt"
}
}
}
{% endaction %}{% assign username = "guest" %}
{% assign password = "guest" %}
{% assign authorization_header = username | append: ":" | append: password | base64 | prepend: "Basic " %}
{% action "http" %}
{
"method": "get",
"url": "https://jigsaw.w3.org/HTTP/Basic/",
"headers": {
"Authorization": {{ authorization_header | json }}
}
}
{% endaction %}{% action "http" %}
{
"method": "get",
"url": "https://api.ipify.org?format=json",
"proxy": "socks5://user:[email protected]:port"
}
{% endaction %}{% log response_type_header: action.run.result.headers['content-type'][0] %}mechanic/user/text
mechanic/actions/perform{% if event.topic == "mechanic/user/text" %}
{% action "http" %}
{
"method": "post",
"url": "https://postman-echo.com/post",
"body": {{ event.data | json }}
}
{% endaction %}
{% else %}
{% action "echo",
response_status: action.run.result.status,
response_content_type: action.run.result.headers['content-type'][0],
response_body: action.run.result.body %}
{% endif %}`code````
code
```→ Unordered List → Ordered List → Plain Text
→ - text → 1. text → text[text](url)> text Upload and download files via FTP, FTPS, or SFTP.
The FTP action can upload and download files via FTP, FTPS, or SFTP. The files to be uploaded are evaluated using file generators. Downloaded file data is available either as an UTF-8 string, or as a base64-encoded string, and can be used in followup task runs via mechanic/actions/perform.
A connecting service like Couchdrop can be used to relay these uploads on to other cloud locations, like Dropbox, Google Drive, and Amazon S3.
A single FTP action may download a maximum of 20MB of data, across all downloaded files.
The user option is always required.
When connecting to an FTP or FTPS server, authenticate with the password option.
When connecting to an SFTP server, authenticate using either password or private_key_pem, or both. PEM certificates may be given directly in the task code:
Both uploads and downloads allow the task author to define file paths. If only the filename is given (e.g. "sample.pdf"), the file will be resolved in the home directory of the user. If a relative path (e.g. "subdirectory/sample.pdf") or absolute path (e.g. "/tmp/sample.pdf") is given, it will be respected accordingly.
Each individual file operation (i.e. each upload or download) will be attempted a maximum of 3 times within the FTP/FTPS/SFTP session, retrying if an error occurs during upload or download.
This example action results in (a) an upload to an absolute path, starting from the server root, (b) an upload to a nested directory within the user's home folder, and (c) an upload to a nested directory in another user's home folder (which may fail, depending on filesystem permissions).
An FTP action returns the following data structure, most useful in combination with mechanic/actions/perform (see ):
Note that each uploaded and downloaded file is keyed by the path provided for that file in the action's options. Downloaded file data is available as a UTF-8 string; for binary data that cannot be represented in UTF-8, use the base64-encoded version, possibly in concert with the filter.
If a server is unavailable for testing, consider using , with . This is a (nearly) configuration-free avenue for testing, using my.couchdrop.io for FTP, FTPS, or SFTP.
Alternatively, can be used to create a public tunnel to a local FTP or SSH server. By running ngrok tcp 22 (adjusting for the appropriate local port), ngrok will generate a temporary public host and port that's appropriate for use while testing.
Uploads are processed before downloads; it can be useful to test by uploading a file, and then immediately downloading it again:
This task compiles all SKUs with their titles and prices, and uploads it as a CSV every night or on demand.
Subscriptions
Code
This tutorial walks you through setting up a custom task in Mechanic, which is called on Contact Form submission on your Shopify frontend, the contents of the form are passed to the task, which emails the contents in CSV format.
Before beginning this tutorial, here's what you'll need:
A Shopify store, which has Mechanic installed (see Mechanic's app store page)
A basic knowledge of Liquid (need a refresher?)
A basic knowledge of JavaScript ()
We have an online store called Mario's Mushrooms, hosted on Shopify. Business is booming, and our mushrooms are being shipped all over the world. Our CEO, Mario, asks us to connect our default Shopify contact form to our legacy customer relationship management (or CRM) system. We are eager to help! While the CRM doesn't have an HTTP API, it can receive CSV imports via email, which it will then import into its database. This gives us our path forward!
We are going to make a task in this cool Shopify app called Mechanic. ;) Here's what the task will do:
The task will add some JavaScript to the online Shopify store, which will capture the contents of the contact form when submitted, and then send those contents over to Mechanic via
Over on the Mechanic side, the task will receive the form contents, and format them as a CSV file
The task will then send an to our CRM system, containing the CSV file as an attachment
Time to build the task! Out of Mechanic's entire toolkit, here's what we'll use:
Start with the tutorial for this part. Webhooks should be configured with respect to the source that supplies them with data, so for this tutorial, use the webhook name "Contact Form" and the event topic "user/webhook/form".
We have options here! The only hard requirement is that we use a POST request to send form data to our webhook. This can be done using pure JavaScript, or using a library like jQuery, or even by using plain HTML to set the form tag's action attribute to our webhook URL.
For this tutorial, we'll use JavaScript. And because we're using Mechanic, we don't even have to edit the theme directly to add in our code – instead, we can use the task editor's feature to have our code automatically loaded into the online storefront. (Under the hood, Mechanic leverages Shopify's API.)
For this tutorial, I created a development store and installed the . I use the contact form that comes with the theme as the form that submits to our webook. You can use any contact form on any theme, or create a form specifically for the purpose of submitting to our webhook.
First things first: we're going to make sure of the element ID, for our contact form. This will be important for writing JavaScript that addresses this form. After investigating, we discover that the form ID is "ContactForm". Easy enough!
Next, we're going to write some JavaScript that listens for thesubmit event of this form – functionally, this means that we're going to wire up some code to run when the form is submitted. The goal: to jump in when the form is submitted, send the form data to our webhook (which will then trigger our Mechanic task), and then allow the form to submit as usual. This way, we add Mechanic functionality without disabling the form's existing behavior.
Let's get started on our JavaScript. In your Mechanic task editor, scroll down and find the "JavaScript for Online Storefront" area. This will add this feature to our task, and we'll be given a place to add in our JavaScript, which will be automatically loaded into our shop frontend.
Copy in the JavaScript below, reading the comments for details on what's going on. Remember the "ContactForm" ID? Here's where we get to use it!
When pasting in this code, a new task option will appear, allowing the user (that's us, for now) to configure the webhook URL. Here's where we use the Mechanic-generated webhook URL from earlier.
With all that in place, save the task. We're leaving the task code empty for right now, and that's okay!
To make sure what data we're working with, let's submit the contact form, and then examine the resulting event data in Mechanic. (It's okay that we hit the captcha prompt; the important part is making sure that we're sending data to Mechanic.)
Heading to the "Events" page of the Mechanic app, we can see our data coming in.
Clicking through to that new event, we can see the event data on the right, reflecting what was in the form at the time of submission. (Depending on the nature of your specific contact form HTML, you might see something slightly different.)
This is perfect! The data we are interested in is inside of an event data property called "contact". This means that, in Liquid, we can access the contact data using {{ event.data.contact }}.
Moving back to the task editor, the first step is to extract this data, and assemble it into something we can format using the filter. Because that filter is made to handle tables of data, this means that we'll create an array of "rows", and fill it with arrays of "columns", and then pass the result into the csv filter.
After that, we'll add an action, configuring it with our CSV data as an attachment. We'll also add a few more task options that will make it easy to reconfigure this task in the future, without having to touch the task code.
Here's how we'll configure the task, using the task option fields that automatically appear based on our task code:
With everything assembled, we head back to the contact form, and make a submission. Back in the task editor, we see a new event appear in "Recent activity", with a green checkmark indicating that the task generated and performed an action.
We did it! We augmented our existing contact form with the ability to send submission data to our new Mechanic task, which relays the data to our CRM system using a CSV email attachment. 🎉
Thanks for reading! If you've got questions or suggestions, join the . :)
If you'd like to quickly pull in all of the task code and configuration we used here, use this task export:









// This code will be loaded on all pages of our store. So, we'll need
// to begin by seeing if the current page has a contact form on it,
// to make sure we're not causing errors by trying to modify a form
// that doesn't exist.
// The `contactForm` variable will either be our form (if it's present
// on this page), or will be null (if it isn't).
const contactForm = document.querySelector('#ContactForm');
// Before Mechanic delivers this JavaScript to the storefront, it first
// evaluates it for Liquid. This means that we get to use the `options`
// object. By using {{ options.mechanic_webhook_url__required }}, we can
// make the webhook URL configurable.
const mechanicWebhookUrl = {{ options.mechanic_webhook_url__required | json }};
// We only want to run all of this if there's a contact form on the page.
if (contactForm) {
// Setting up a flag for later - keep reading!
let submittedToMechanic = false;
contactForm.addEventListener(
'submit',
(event) => {
// We're going to prevent the form submit from doing its normal
// normal. We'll re-submit the form in a second, after we've
// submitted data to Mechanic.
event.preventDefault();
// We'll use fetch to make our POST request:
// https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Fetch_API
fetch(
mechanicWebhookUrl,
{
method: 'POST',
body: new FormData(contactForm),
}
).then((response) => {
console.log('Sending data to Mechanic: Success!', response);
}).catch((error) => {
console.error('Sending data to Mechanic: Error!', error);
}).finally(() => {
// Now that we're done with sending our data to Mechanic,
// we're going to manually submit the contact form. This won't
// trigger the "submit" event again; it'll just run the form's
// usual submit behavior.
contactForm.submit();
});
},
);
}{% assign rows = array %}
{% assign header = array %}
{% assign header[0] = "Name" %}
{% assign header[1] = "Email" %}
{% assign header[2] = "Phone Number" %}
{% assign header[3] = "Message" %}
{% assign rows[rows.size] = header %}
{% assign row = array %}
{% assign row[0] = event.data.contact.name %}
{% assign row[1] = event.data.contact.email %}
{% assign row[2] = event.data.contact.phone %}
{% assign row[3] = event.data.contact.body %}
{% assign rows[rows.size] = row %}
{% assign csv_data = rows | csv %}
{% action "email" %}
{
"to": {{ options.recipient_email_address__email_required | json }},
"subject": {{ options.email_subject__required | json }},
"body": {{ options.email_body__required_multiline | strip | newline_to_br | json }},
"attachments": {
{{ options.csv_attachment_filename__required | replace: ".csv", "" | append: ".csv" | json }}: {{ rows | csv | json }}
}
}
{% endaction %}{"name":"Receive contact form for CRM","options":{"recipient_email_address__email_required":"[email protected]","email_subject__required":"Contact form submission for CRM: {{ \"now\" | date: \"%Y-%m-%d %H:%M\" }}","email_body__required_multiline":"Hello,\n\nPlease find the attached CSV. Thanks!\n\n-Mechanic, for {{ shop.name }}","csv_attachment_filename__required":"contact-form-for-crm-{{ \"now\" | date: \"%s\" }}","mechanic_webhook_url__required":"https://webhooks.mechanic.dev/00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000"},"subscriptions":["user/webhook/form"],"subscriptions_template":null,"script":"{% assign rows = array %}\n\n{% assign header = array %}\n{% assign header[0] = \"Name\" %}\n{% assign header[1] = \"Email\" %}\n{% assign header[2] = \"Phone Number\" %}\n{% assign header[3] = \"Message\" %}\n{% assign rows[rows.size] = header %}\n\n{% assign row = array %}\n{% assign row[0] = event.data.contact.name %}\n{% assign row[1] = event.data.contact.email %}\n{% assign row[2] = event.data.contact.phone %}\n{% assign row[3] = event.data.contact.body %}\n{% assign rows[rows.size] = row %}\n\n{% assign csv_data = rows | csv %}\n\n{% action \"email\" %}\n {\n \"to\": {{ options.recipient_email_address__email_required | json }},\n \"subject\": {{ options.email_subject__required | json }},\n \"body\": {{ options.email_body__required_multiline | strip | newline_to_br | json }},\n \"attachments\": {\n {{ options.csv_attachment_filename__required | replace: \".csv\", \"\" | append: \".csv\" | json }}: {{ rows | csv | json }}\n }\n }\n{% endaction %}","docs":null,"halt_action_run_sequence_on_error":false,"liquid_profiling":false,"online_store_javascript":"// This code will be loaded on all pages of our store. So, we'll need\n// to begin by seeing if the current page has a contact form on it,\n// to make sure we're not causing errors by trying to modify a form\n// that doesn't exist.\n\n// The `contactForm` variable will either be our form (if it's present\n// on this page), or will be null (if it isn't).\nconst contactForm = document.querySelector('#ContactForm');\n\n// Before Mechanic delivers this JavaScript to the storefront, it first\n// evaluates it for Liquid. This means that we get to use the `options`\n// object. By using {{ options.mechanic_webhook_url__required }}, we can\n// make the webhook URL configurable.\nconst mechanicWebhookUrl = {{ options.mechanic_webhook_url__required | json }};\n\n// We only want to run all of this if there's a contact form on the page.\nif (contactForm) {\n\n // Setting up a flag for later - keep reading!\n let submittedToMechanic = false;\n \n contactForm.addEventListener(\n 'submit',\n (event) => {\n // We're going to prevent the form submit from doing its normal\n // normal. We'll re-submit the form in a second, after we've\n // submitted data to Mechanic.\n event.preventDefault();\n\n // We'll use fetch to make our POST request:\n // https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Fetch_API\n fetch(\n mechanicWebhookUrl,\n {\n method: 'POST', \n body: new FormData(contactForm),\n }\n ).then((response) => {\n console.log('Sending data to Mechanic: Success!', response);\n }).catch((error) => {\n console.error('Sending data to Mechanic: Error!', error);\n }).finally(() => {\n // Now that we're done with sending our data to Mechanic,\n // we're going to manually submit the contact form. This won't\n // trigger the \"submit\" event again; it'll just run the form's\n // usual submit behavior.\n contactForm.submit();\n });\n },\n );\n}","order_status_javascript":null,"perform_action_runs_in_sequence":false,"shopify_api_version":"2021-01"}password
String, optional
The password for authentication
uploads
Hash, optional
An object whose keys are file paths (relative or absolute), and whose values are
downloads
Array, optional
File path strings (relative or absolute) to download
protocol
"ftp", "ftps", or "sftp"
The protocol to use for connection; inferred if omitted
host
String, required
The hostname or IP address of the destination server
port
Number, optional
The server port to connect to
user
String, required
The username for authentication
mode
String, optional
May be set to "ascii"; defaults to "binary"
verify
Boolean, optional
May be set to false to ignore SSL certificate errors
private_key_pem
String, optional
A complete PEM-formatted private key for authentication
verify
Boolean, optional
May be set to true in combination with "known_hosts" to validate the host
known_hosts
String, optional
An sshd-compatible known_hosts file (docs, helpful article)
accept user configuration via options. Options are created dynamically, by reference: each option referenced in a task's results in that option being added to the task's configuration form. In the option reference {{ options.foo_bar__required }}, the option key is foo_bar__required. The appearance and behavior of the option's form element is based on flags in in the option key – in this example, only the "required" flag is in use.
Mechanic flags provide only limited option validation. A task may define , by rendering error objects according to the task's its own validation logic.
{% capture private_key_pem %}
-----BEGIN OPENSSH PRIVATE KEY-----
l0UGrDQWWbOpUsLENHwD5ya478pmRXarmDj5Wh31B54nmuq7be4ZKD5eh9nEV42JCl4mX6
...
pZ/WFoT82brhooSfJDue14C0Y=
-----END OPENSSH PRIVATE KEY-----
{% endcapture %}
{% action "ftp" %}
{
"host": "example.com",
"port": 22,
"user": "sftp_user",
"private_key_pem": {{ private_key_pem | json }}
"uploads": {
"success.txt": "hooray!"
}
}
{% endaction %}{% action "ftp" %}
{
...
"uploads": {
"/absolute/path/to/success.txt": "hooray!",
"relative/path/to/success.txt": "hooray!",
"../another/relative/path/to/success.txt": "hooray!"
}
}
{% endaction %}{
"log": "connect: ftp.couchdrop.io, 21\n< 220 Couchdrop FTPD\n> USER ********\n< 331 Username ok, send password.\n> PASS ********\n< 230 Welcome ********\n> TYPE I\n< 200 Type set to: Binary.\n> TYPE I\n< 200 Type set to: Binary.\n> PASV\n< 227 Entering passive mode (178,128,9,71,234,153).\n> STOR journal.txt\n< 125 Data connection already open. Transfer starting.\n< 226 Transfer complete.\n> TYPE I\n< 200 Type set to: Binary.\n> TYPE I\n< 200 Type set to: Binary.\n> PASV\n< 227 Entering passive mode (178,128,9,71,234,98).\n> STOR table.csv\n< 125 Data connection already open. Transfer starting.\n< 226 Transfer complete.\n> TYPE I\n< 200 Type set to: Binary.\n> TYPE I\n< 200 Type set to: Binary.\n> PASV\n< 227 Entering passive mode (178,128,9,71,234,135).\n> STOR invoice.pdf\n< 125 Data connection already open. Transfer starting.\n< 226 Transfer complete.\n> TYPE I\n< 200 Type set to: Binary.\n> TYPE I\n< 200 Type set to: Binary.\n> PASV\n< 227 Entering passive mode (178,128,9,71,234,101).\n> STOR secure.zip\n< 125 Data connection already open. Transfer starting.\n< 226 Transfer complete.\n> TYPE I\n< 200 Type set to: Binary.\n> TYPE I\n< 200 Type set to: Binary.\n> PASV\n< 227 Entering passive mode (178,128,9,71,234,100).\n> STOR external.jpg\n< 125 Data connection already open. Transfer starting.\n< 226 Transfer complete.\n> TYPE I\n< 200 Type set to: Binary.\n> TYPE I\n< 200 Type set to: Binary.\n> PASV\n< 227 Entering passive mode (178,128,9,71,234,183).\n> RETR journal.txt\n< 125 Data connection already open. Transfer starting.\n< 226 Transfer complete.\n> TYPE I\n< 200 Type set to: Binary.\n> TYPE I\n< 200 Type set to: Binary.\n> PASV\n< 227 Entering passive mode (178,128,9,71,234,149).\n> RETR table.csv\n< 125 Data connection already open. Transfer starting.\n< 226 Transfer complete.\n> TYPE I\n< 200 Type set to: Binary.\n",
"uploads": {
"invoice.pdf": {
"size": 7232
},
"secure.zip": {
"size": 205
},
"external.jpg": {
"size": 27661
}
},
"downloads": {
"journal.txt": {
"size": 12,
"data": "hello world!",
"data_base64": "aGVsbG8gd29ybGQh"
},
"table.csv": {
"size": 27,
"data": "Title,SKU\nRed T-Shirt,TEE-R",
"data_base64": "VGl0bGUsU0tVClJlZCBULVNoaXJ0LFRFRS1S"
}
}
}{% action "ftp" %}
{
"host": "ftp.couchdrop.io",
...
"uploads": {
"hello-world.txt": "hello world!"
},
"downloads": [
"hello-world.txt"
]
}
{% endaction %}mechanic/scheduler/daily
mechanic/user/trigger{% assign csv_rows = array %}
{% assign header = "SKU,Title,Price" | split: "," %}
{% assign csv_rows[0] = header %}
{% for product in shop.products %}
{% for variant in product.variants %}
{% assign title = variant.title %}
{% if title == "Default Title" %}
{% assign title = product.title %}
{% endif %}
{% assign row = array %}
{% assign row[row.size] = variant.sku %}
{% assign row[row.size] = title %}
{% assign row[row.size] = variant.price %}
{% assign csv_rows[csv_rows.size] = row %}
{% endfor %}
{% endfor %}
{% capture filename %}product-export-{{ "now" | date: "%Y-%m-%d" }}.csv{% endcapture %}
{% action "ftp" %}
{
"host": "example.com",
"port": 21,
"user": "anonymous",
"password": null,
"uploads": {
{{ filename | json }}: {{ csv_rows | csv | json }}
}
}
{% endaction %}options variable, which is a hash having key-value pairs for each option key and option value. The option key must only contain ASCII numbers, lowercase letters, and underscores. The option key is reformatted for use as the option name presented to the user – underscores are replaced by spaces, and the entire line is sentence-cased.name
Lowercase letters, numbers, and underscores only.
send_after
flag
One or more tokens that customise the field (see below).
required, date, picker_product
Because option keys are registered via static analysis, options must each be referenced using a standard lookup (e.g. options.foobar) at least once.
Options are displayed to the user in the order in which they are first referenced in the task code.
Because this may not result in a natural sequence, it can be useful to prefix task code with a comment block, explicitly referencing each option so as to force the overall order.
Option flags control how an option appears and behaves in a task's configuration form, and also control the type and format of the option value.
Many flags may be combined with other flags, for more nuanced control.
If no flags are used for an option, an option will be made available as a plain text field, and the option value will be a string.
The special userform flag does not change the input type or validation; it simply marks an option as one that should appear on the Run-task form (topic mechanic/user/form) in additions to the general task options screen.
Input types
Choose a specific control and value type (date picker, slider, select list, …). Exactly one input‑type flag should be used.
Form modifiers
Fine‑tune how the control looks or validates (required, multiline, etc.).
Auxiliary flags
Extra behaviour for certain input types (future‑only dates, multi‑select choices, etc.).
(none - default)
Single‑line text
string
options.subject
multiline
Multiline text box
string
options.body__multiline
boolean
Checkbox
true/false
Use ordinal tokens to define values:
Ordinals (o1, o2, …) determine display order. Underscores inside values are preserved.
min<number> – required
max<number> – required
step<number> – optional (defaults to 1).
Append _array for multi‑select.
Unsupported resources are rejected during validation.
required
Any
Field must be filled before Save.
email
text
Adds email placeholder and basic email format check.
userform
Any
Shows this option on Run task form (mechanic/user/form).
futureonly
date, datetime
Picker disallows past dates.
Required fields must not be empty.
Range sliders need both min and max.
Pickers only allow product, variant, or collection.
Email inputs are matched against a basic regex.
Custom rules? Learn more about custom validation.
Options that allow text input are evaluated for Liquid when a task processes an event. Liquid evaluation for options occurs before it occurs for task code, which means that any Liquid variables created by task code are not available to task options.
Liquid code in task options have access to the same set of environment variables that are made available to the task code, including event, shop, cache, and any event subject variables.
Text input
options.subject__required
"Welcome!"
Checkbox
options.newsletter__boolean
false
Key–value map
options.headers__keyval
Getting a plain string (strip the offset)
<name>[__<flag>[ _<flag> ... ]]{% comment %}
Option order:
{{ options.api_key__required }}
{{ options.mode__select_o1_test_o2_live }}
{{ options.webhooks__array }}
{% endcomment %}<name>__select_o1_basic_o2_pro_o3_enterprise
│ │ │ │
│ │ │ └───── value #2
│ │ └──────── ordinal marker
│ └──────────── value #1
└─────────────── ordinal marker<name>__picker_<product|variant|collection>[_array]{{ options.launch_date__date | date: "%Y-%m-%d" }}
⇒ 2025-05-06
{{ options.quiet_at__time | date: "%H:%M" }}
⇒ 00:25
{{ options.party__datetime | date: "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M" }}
⇒ 2031-04-22 15:13{{ options.party__datetime | date: tz: "UTC" }}
⇒ 2031-04-22T19:13:00Z {offset shifted +4 h}
{{ options.quiet_at__time | date: "%H:%M %Z", tz: "America/Vancouver" }}
⇒ 21:25 PDToptions.enabled__boolean
number
Numeric input (step=1)
number
options.count__number
code
Code‑formatted text area
string
options.script_snippet__code_multiline
keyval
Key → value repeater
hash
options.headers__keyval
array
Value repeater
array
options.tags__array
date
Calendar picker
"YYYY‑MM‑DD"
options.launch_date__date
datetime
Date+time picker
"YYYY‑MM‑DDTHH:MM"
options.send_at__datetime
time
Time‑only picker
"HH:MM"
options.quiet_time__time
color
Hex colour picker
"#RRGGBB"
options.theme_color__color
range_minX_maxY_stepZ
Slider + number box
number
options.qty__range_min0_max100_step5
select
Single‑choice dropdown
string
options.plan__select_o1_basic_o2_pro
choice
Radio buttons
string
options.tier__choice_o1_gold_o2_silver
multiselect
Checkbox list
array[string]
options.channels__multiselect_o1_email_o2_sms
picker_<resource>
Shopify resource picker
gid string
options.product__picker_product
picker_<resource>_array
Multi‑select resource picker
array[gid]
options.products__picker_product_array
{ "X-Env": "staging" }
String list
options.tags__array
["vip","wholesale"]
0–100 slider
options.score__range_min0_max100
42
Colour picker
options.bg__color
"#336699"
Dropdown
options.plan__select_o1_basic_o2_pro
"basic"
Multi‑select
options.channels__multiselect_o1_email_o2_sms
["email","sms"]
Product picker
options.promo__picker_product
"gid://shopify/Product/123"
Product list
options.products__picker_product_array
[ "gid://…/1", "gid://…/2" ]
Date
options.go_live__date_required
"2025-05-06"
Time
options.quiet_at__time
"00:25"
Datetime
options.party__datetime
"2031-04-22T15:13:00"